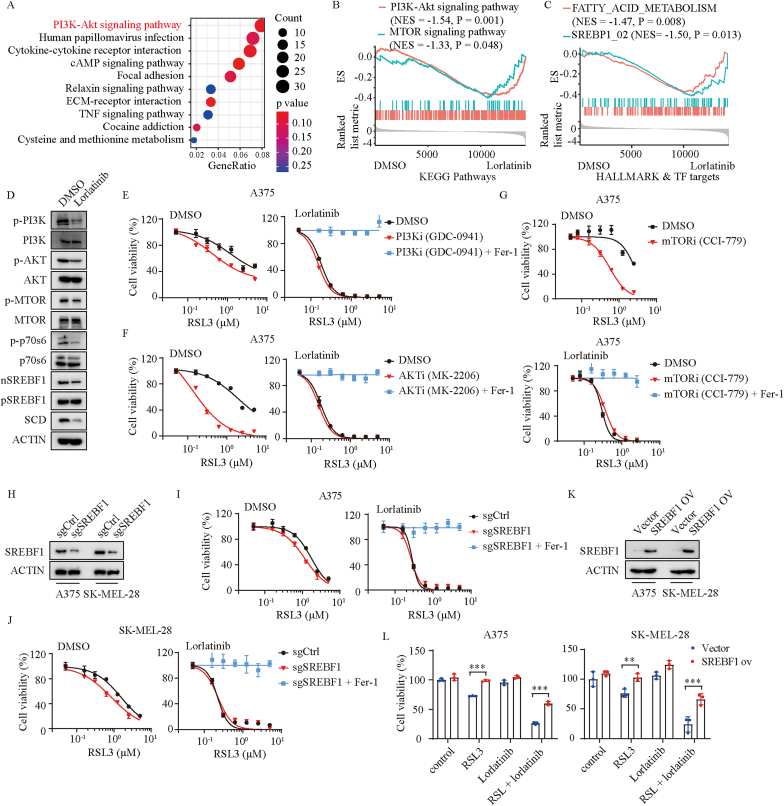
Fig. 4.
Lorlatinib inhibits the expression of SCD via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling.
(A) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed genes between DMSO and lorlatinib treated A375 cells. (B) GSEA showing that PI3K-Akt and MTOR signaling pathways were down regulated in lorlatinib treatment group. (C) GSEA showing that FATTY_ACID_METABOLISM and SREBP1 signaling were down regulated in lorlatinib treatment group. (D) Western blotting analysis of the indicated proteins in A375 cells treated with DMSO or lorlatinib (5 μM) for 12 h. (E) Dose response of RSL3-induced death of DMSO or PI3Ki (GDC-0941) treated- A375 cells in the absence or presence of lorlatinib for 6 h. (F) Dose response of RSL3-induced death of DMSO or AKTi (MK-2206) treated- A375 cells in the absence or presence of lorlatinib for 6 h. (G) Dose response of RSL3-induced death of DMSO or mTORi (CCI-779) treated- A375 cells in the absence or presence of lorlatinib for 6 h. (H) SREBP1 protein levels were quantified by western blotting in control (sgCtrl) and SREBP1 deficient (sgSREBF1) cells. (I-J) Dose response of RSL3-induced death of sgCtrl and sgSREBF1 A375 (I) or SK-MEL-28 (J) cells in the presence of DMSO or lorlatinib (5 μM) for 6 h. (K) SREBP1 protein levels were quantified by western blotting in cells with control (vector) or SREBF1 overexpression (SREBF1 ov). (L) Viability of the indicated cells with control or SREBF1 overexpression after treatment with RSL3 (2.5 μM), lorlatinib (2.5 μM), or RSL3 + lorlatinib. P values were calculated using two-way ANOVA analysis in L. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.