Figure 4.
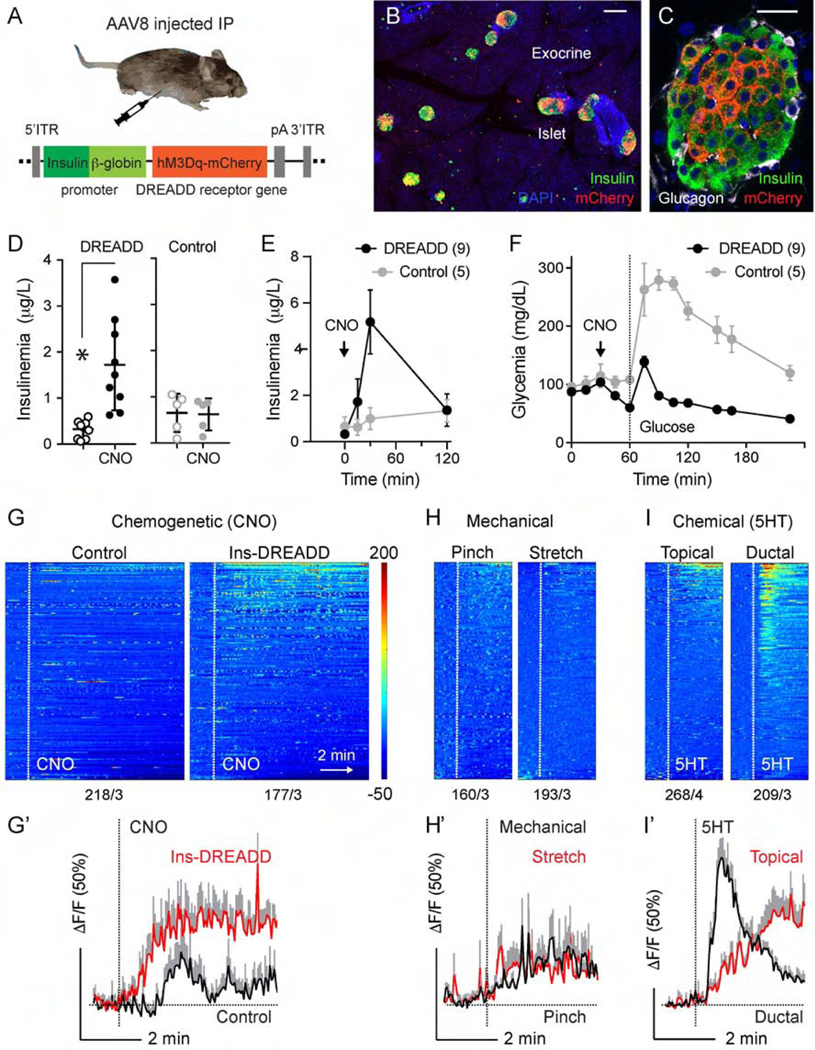
Chemogenetic stimulation of pancreatic beta cells activates vagal sensory neurons. (A) Cartoon of the chemogenetic AAV8 vector that was injected intraperitoneally into Pirt-GCaMP6 mice. (B-C) Pancreatic sections from AAV-8 infected mice, immunostained for RFP (DREADD-mCherry, red), insulin (green), Dapi (blue). (D) Changes in blood insulin levels in response to intraperitoneal injection of the DREADD agonist clozapine N-oxide (CNO, 5 mg/kg) in 12 h fasted DREADD-expressing (n = 9) and control (n = 5) mice (Student’s t-test). (E-F) Blood insulin levels and glucose excursion during an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test preceded by CNO injection (arrow) in DREADD-expressing (n = 9) and control (n = 5) mice. (G-I) Heatmaps and average traces showing in vivo Ca2+ responses of nodose ganglion neurons to intraperitoneal administration of CNO in control and DREADD-expressing animals (G), to mechanical (pinch or stretch, H), and to chemical stimulation (5HT, I). Each row is a single cell, x-axis is time, and response magnitude dF/F (%) is shown in color scale, where fluorescence intensity increases from blue to red. Numbers of neurons/animals are indicated under each heatmap. G’-I’ are average traces (+/− SEM) of the top 15 responding neurons shown in G-I. Scale bars, (B) 100 μm and (C) 20 μm.