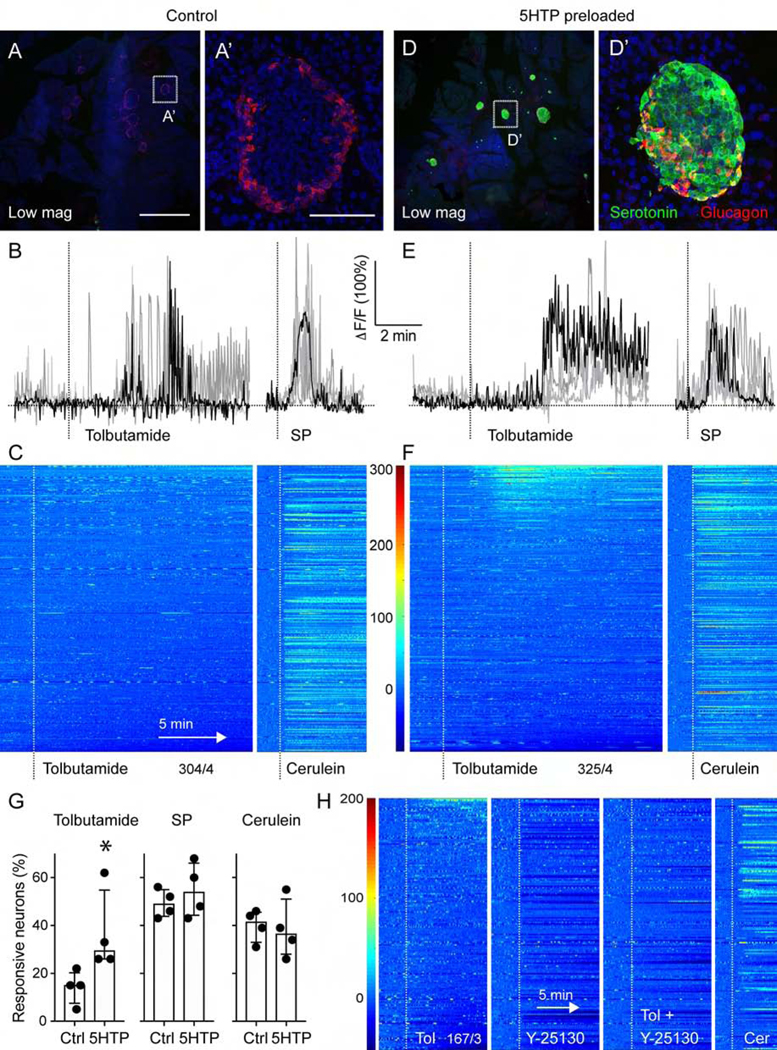
Figure 7.
Vagal sensory neurons responses to beta cell stimulation are amplified by 5HTP-preloading. (A, D) z-stacks of confocal images of pancreatic sections from untreated mice (A) and mice preloaded with 5HTP (30 mg/kg; D). Serotonin immunostaining (green) is increased in islets (glucagon in red) from treated mice. A’ and D’ are higher magnifications of A and D. Note that endogenous levels of serotonin in control tissue are not visible because imaging settings were adjusted for the increased serotonin levels in 5HTP-preloaded tissue. (B, E) Representative traces of Ca2+ responses of nodose ganglion neurons to topical stimulation of the pancreas with tolbutamide (5 mM) and substance P (100 μM) in control (B) and 5HTP-preloaded (E) animals. (C, F) Heatmaps showing responses of nodose ganglion neurons to pancreatic stimulation with tolbutamide and cerulein in control mice (C, 304 neurons, n = 4 mice) and mice preloaded with 5HTP (F, 325 neurons, n = 4 mice). Each row is a single cell, x-axis is time, dF/F is color. (G) Quantification of the percentage of neurons responding to pancreatic stimulation in control and 5HTP preloaded animals (n = 4 for each group, Mann Whitney test, median +/− 95% CI). (H) Average trace of 16 nodose ganglion neurons that showed an increase in activity in response to tolbutamide stimulation of the pancreas. The Htr3 receptor antagonist Y-25130 (1 mM) inhibited responses to tolbutamide and lowered overall neuronal baseline activity level. Responses to cerulein were not affected. Scale bars, (A, D) 1 mm and (A’, D’) 50 μm.