Figure 1 |. DNA strand breaks are enriched at human centromeres.
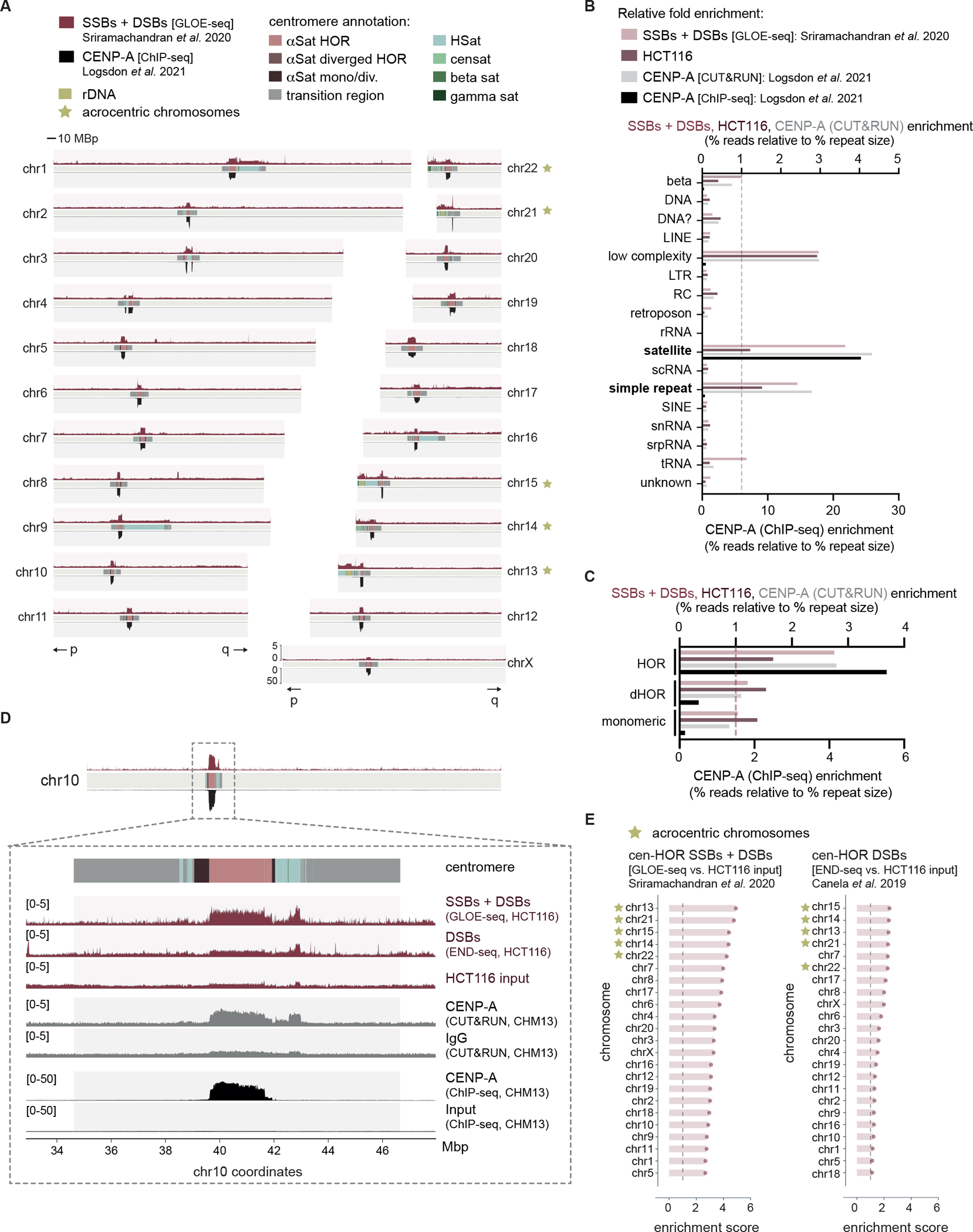
(A) Alignment of publicly available next generation sequencing data detecting DNA strand breaks (GLOE-seq25) above and CENP-A localization (ChIP-seq28) below across 22 autosome chromosomes and chromosome X of the human T2T-CHM13 reference assembly. Centromeric regions are composed of alpha satellites within higher order repeats (αSat HORs), alpha satellites within diverged HORs (αSat diverged HORs), monomeric / diverged alpha satellites (αSat mono/div.), human satellites (HSat), beta satellites (beta sat), gamma satellites (gamma sat), transition regions, other satellites (censat) and ribosomal DNA arrays (rDNA). p and q chromosome arms indicated below. (B) Fold enrichment of DNA breaks, HCT116 input and CENP-A (both CUT&RUN and ChIP-seq) reads across all annotated repeat types of the T2T-CHM13 reference genome. (C) Fold enrichment of DNA breaks, HCT116 input and CENP-A CUT&RUN reads over alpha satellites annotated as being either part of HORs, divergent HORs (dHOR) or monomeric. (D) Inset of chr10 centromere depicting total DNA breaks (GLOE-seq25) and DNA DSBs (END-seq27) with the corresponding input cell line (HCT116), as well as CENP-A localization (CUT&RUN above, ChIP-seq below) with the corresponding negative control (IgG above, ChIP-seq input below)28. (E) Enrichment scores of GLOE-seq or END-seq in HCT116 cells across human centromere HORs. Enrichment scores were calculated as the sums of mapped reads within centromeric HORs of each chromosome relative to that of the corresponding input control, after normalizing to read depth. Acrocentric chromosomes containing rDNA arrays are marked as indicated. See also Figures S1 and S2.
