Figure 6. FGF21 exerts its anti-intoxicant activity through noradrenergic neurons.
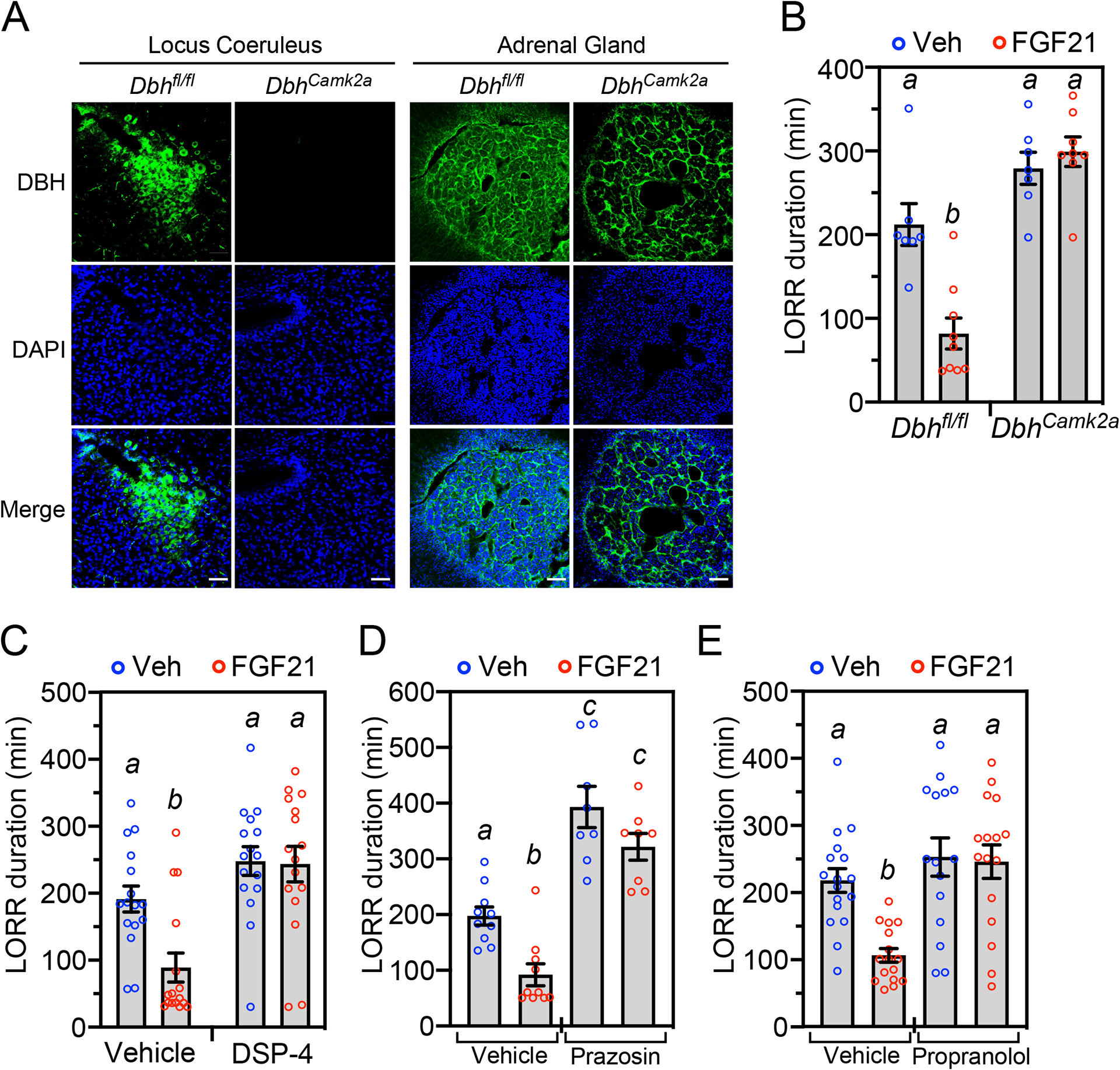
(A) Immunostaining for DBH in locus coeruleus and adrenal from control (Dbhfl/fl) and neuron-specific Dbh−/− (DbhCamk2a) mice. DAPI staining (blue) and merge of the two is shown below. Scale bars represents 50 μM.
(B) Dbhfl/fl and DbhCamk2a mice were administered ethanol (5 g/kg, oral gavage) followed 1 hour later by injection of vehicle or FGF21 (1 mg/kg, i.p.). Loss of righting reflex (LORR) duration was measured after FGF21 or vehicle administration (n = 7–9 mice/group).
(C) Wild-type (WT) mice were injected with DSP-4 (50 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle. Two days later, the mice were administered ethanol (5 g/kg, oral gavage) followed 1 hour later by injection of FGF21 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle (n = 16 mice/group). LORR duration was measured after FGF21 or vehicle administration.
(D) WT mice were administered ethanol (5 g/kg, oral gavage) followed 1 hour later by injection of vehicle, FGF21 (1 mg/kg, i.p.), prazosin (0.8 mg/kg) or FGF21+prazosin (n = 8–10 mice/group). LORR duration was measured after vehicle or FGF21 administration.
(E) The experiment was performed as in (B) except mice were injected with vehicle, FGF21 (1 mg/kg, i.p.), propranolol (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or FGF21+propranolol (n = 15–17 mice/group). LORR duration was measured after vehicle or FGF21 administration.
All data represent the mean ± SEM. Different lowercase letters indicate statistical significance (P < 0.05) by two-way ANOVA.
See also Figure S2.
