Figure 1.
Susceptibility of various cell types to infection by spike-containing viral pseudo-particles and genuine human coronaviruses
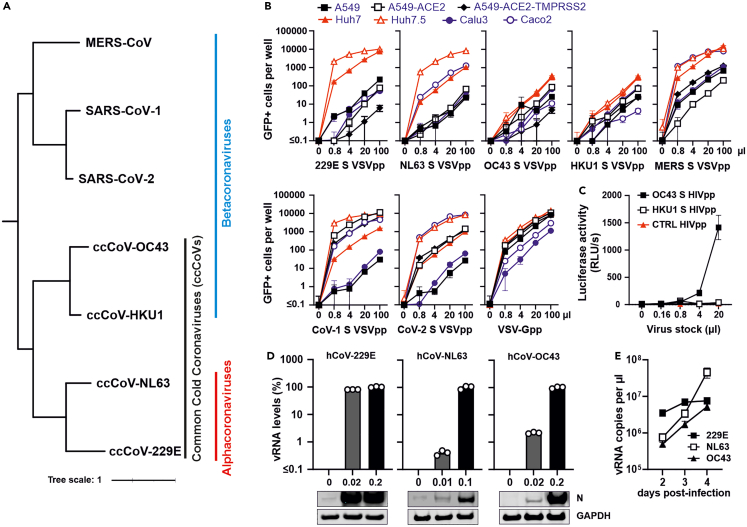
(A) Phylogenetic tree of human coronaviruses. Distance-based relationship inference based on representative full-genome nucleotide sequences of the indicated human coronaviruses.
(B) Automatic quantification of infection events of A549, A549-ACE-2, A549-ACE-2-TMPRSS2, Huh7, Huh7.5, Calu3 and Caco2 cells transduced with different quantities of VSVΔG-GFP stocks pseudo-typed with hCoV-229E,-NL63,-OC43, HKU1, MERS, CoV-1 and CoV-2 spike proteins or VSV-G for control. Cytation was performed at 24 h post-infection.
(C) Lentiviral particles containing hCoV-OC43 or-HKU1 S proteins were generated by cotransfection of HEK293T cells with spike expression plasmids and a pNL1_HIV-1_NL4-3-Δenv-fluc construct. Huh7 cells were infected with the indicated amounts of HIVpp and luciferase activity was measured at 48 h post-infection.
(D) Huh7 cells were infected with genuine hCoV-229E, hCoV-NL63 and hCoV-OC43 at the indicated MOIs. Viral RNA levels in cellular extracts were determined by qRT-PCR 48 h post-infection. The lower panel shows immunoblots of the corresponding whole cell lysates stained with anti-229E N,-NL63 N or-OC43 N and anti-GAPDH.
(E) Huh7 cells were infected with hCoV-229E (MOI 0.01), hCoV-NL63 (MOI 0.05) and hCoV-OC43 (MOI 0.01). Viral RNA in supernatants harvested at 2, 3 and 4 days post-infection was determined by qRT-PCR. Bars represent the mean of three independent experiments (±SEM).