Figure 4. SAYSD1 recognizes ribosome directly via an N-terminal segment.
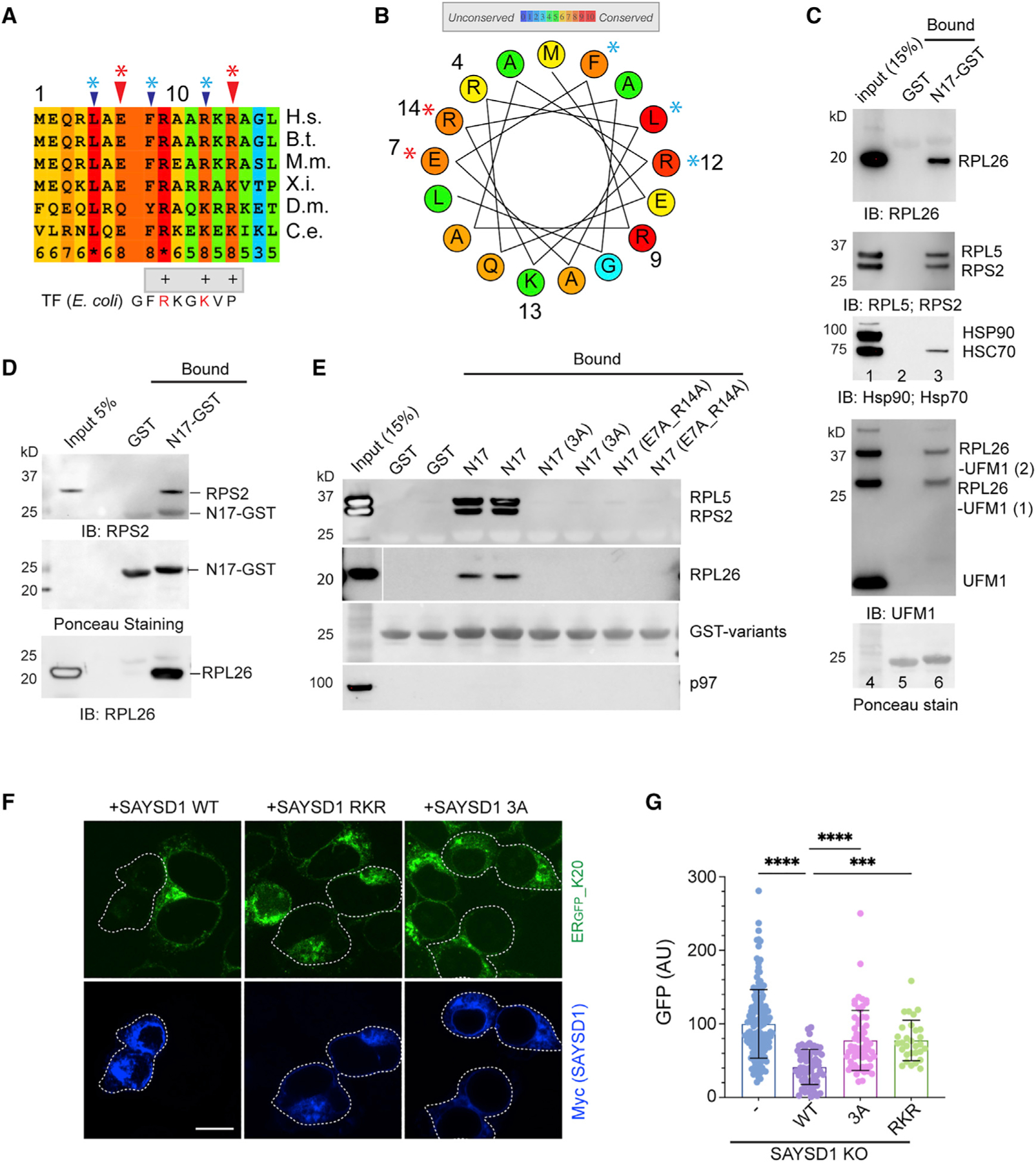
(A) Sequence alignment of the N17 domain of SAYSD1. The arrows indicate the two groups of conserved residues mutated in the study.
(B) A helix wheel view of the SAYSD1 N17 domain. Colors indicate the degree of conservation. Asterisks indicate residues mutated.
(C and D) GST-N17 interacts with ribosome directly. (C) GST-N17 or GST immobilized on glutathione beads were incubated with 293T cell extract. Precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) As in (C) except that ribosome purified from rabbit reticulocyte lysate was used.
(E) The conserved residues in N17 are required for ribosome binding. The indicated GST-tagged N17 variants or GST was immobilized in duplicate and incubated with 293T cell lysate. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using indicated antibodies.
(F and G) SAYSD1 ribosome binding is required for efficient turnover of ERGFP_K20. (F) SAYSD1 KO cells expressing ERGFP_K20 were transfected with the indicated DNA and imaged. SAYSD1-positive cells are highlighted by dashed lines. Scale bar, 10 μm. The graph in (G) shows the quantification of randomly imaged cells from two independent experiments. Error bars, means ± SD; ****p < 0.0001; ***p < 0.001 by unpaired Student’s t test.
