Fig. 5.
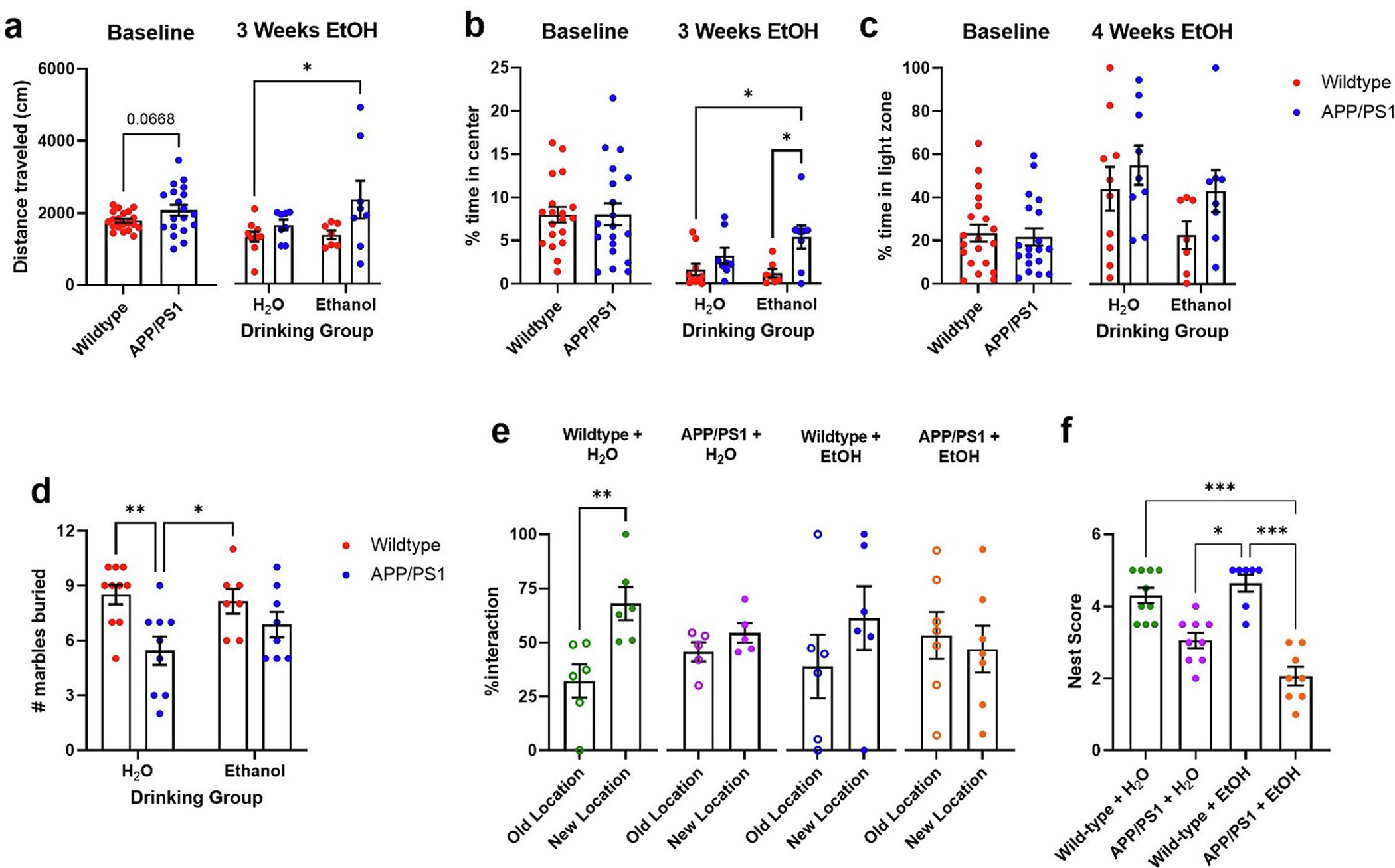
Chronic ethanol consumption alters anxiety-related and dementia-related behaviors in APP/PS1 mice. a) At baseline, APP/PS1 mice showed a trend towards increased locomotor activity during the OFA (unpaired t-test, p = 0.0668). After 3 weeks of ethanol exposure APP/PS1 mice showed more locomotor activity than other groups. b) There were no differences in the % time spent in the center zone at baseline. After 3 weeks of ethanol treatment, APP/PS1 mice spent more time in central zone than wildtype controls. c) Mice exhibited no differences spent in the light zone in the LD box at baseline or following treatment. d) H2O-treated APP/PS1 mice buried more marbles than wildtype controls. e) H2O-treated wildtype spent significantly more time interacting with the relocated object than with the object in the familiar location (unpaired t-test, p = 0.0078), while other groups spent similar amounts of time interacting with both objects. f) APP/PS1 mice + ETOH made poorer nests compared to wildtype mice. 2-way ANOVA revealed differences in nest building scores between groups after 9 weeks of EtOH treatment. (Kruskal-Wallis test: p < 0.0001). Wildtype + H2O, n = 10; APP/PS1 + H2O, n = 9; Wildtype + EtOH, n = 7; APP/PS1 + EtOH, n = 8. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
