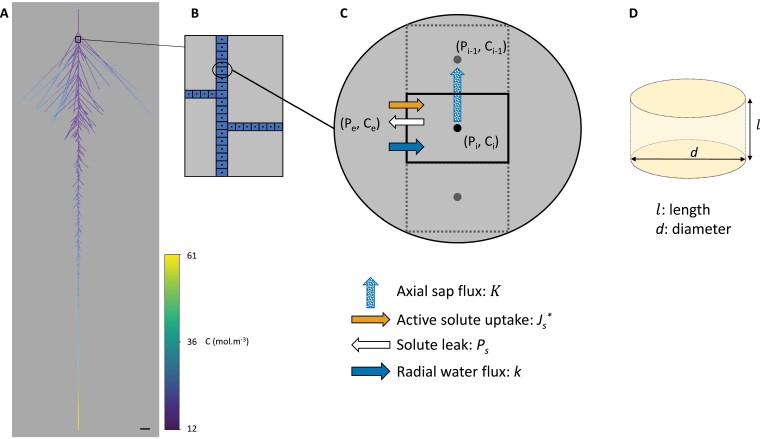
Fig. 1.
Modeling water and solute transport within realistic RSAs of maize primary roots. (A) RSA of a CTR root with a heat map representation of the solute concentration. Scale bar=10 mm. (B) The architecture was discretized in representative elementary volumes (REVs). (C) Sketch of the different fluxes in and out of a REV, for Pe>Pi>Pi–1 and Ci>Ce, and in the absence of PEG. The sap flow along the xylem vessels is characterized by the axial conductance K profile. The water flow across the peripheral root tissues and into the xylem is characterized by the radial hydraulic conductivity k. The solutes are taken up into the xylem vessels at a constant rate Js*. Ps is the tissue permeability of the solutes. (D) REV geometry characterized by its length l and its diameter d that depends on the root order (axial or first-order lateral root).