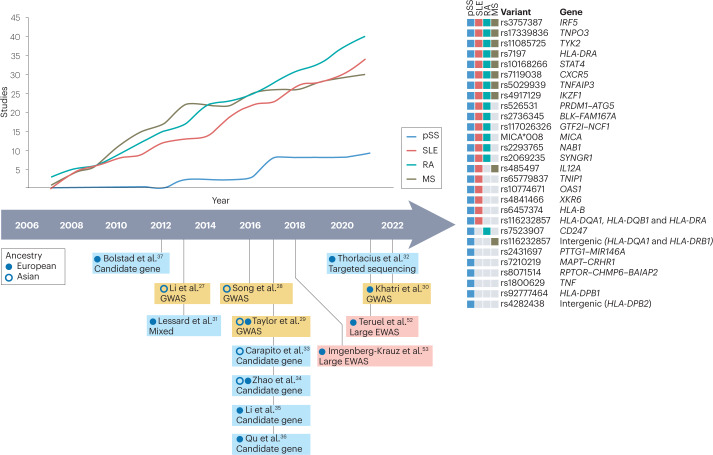
Fig. 2. Studies identifying genetic risk loci of genome-wide significance.
An increasing number of studies on primary Sjögren syndrome (pSS) and selected other autoimmune diseases are registered in the genome-wide association studies (GWAS) catalogue205. However, the number of studies that have identified genetic variants of genome-wide significance in pSS is still low compared with other autoimmune diseases. In the timeline, key papers in pSS that identify novel genetic loci at genome-wide significance are indicated, as well as large-scale epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS) that included ≥100 patients with pSS. Some genetic risk loci identified for pSS are also associated with other autoimmune disease. Many of the non-HLA variants associated with pSS are also associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), whereas fewer variants overlap with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or multiple sclerosis (MS). Some variants seem to specifically increase the risk of pSS30,205.