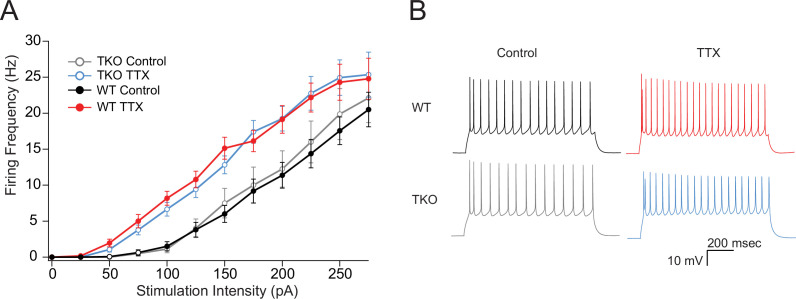
Figure 5. The effects of TTX on intrinsic excitability are not altered in TKO pyramidal neurons.
(A) Comparisons of frequency-current relationships for layer five pyramidal neurons in control (black, closed circles) and TTX-treated (red, closed circles) WT slices, and in control (gray, open circles), and TTX-treated (blue, open circles) TKO slices, N = 27 cells for WT TTX, N = 16 for WT control, N = 8 for TKO control, and N = 17 for TKO TTX; error bars are SEM. Two-day TTX treatment increases intrinsic excitability in both WT and TKO slice cultures to a similar extent. A three-way mixed ANOVA with between subjects factors of treatment and genotype, and a within subjects factor of current level, revealed significant main effects for TTX treatment (F(1,60) = 18.1, p = 7.3e−05) and current level (F(11,660) = 2.3e−190) but not for genotype (F(1,60) = 0.06, p = 0.94). There was a significant interaction between treatment and current level (p = 0.06) but not for interactions of genotype with current level (p = 0.93) or with both current level and treatment (p = 0.99). (B) Example traces of a train of action potentials from a pyramidal neuron in response to a 175 pA 0.5 s depolarizing current injection in control (left), TTX-treated (right), WT (top), or TKO (bottom) slices. TKO, triple knockout; WT, wild-type.