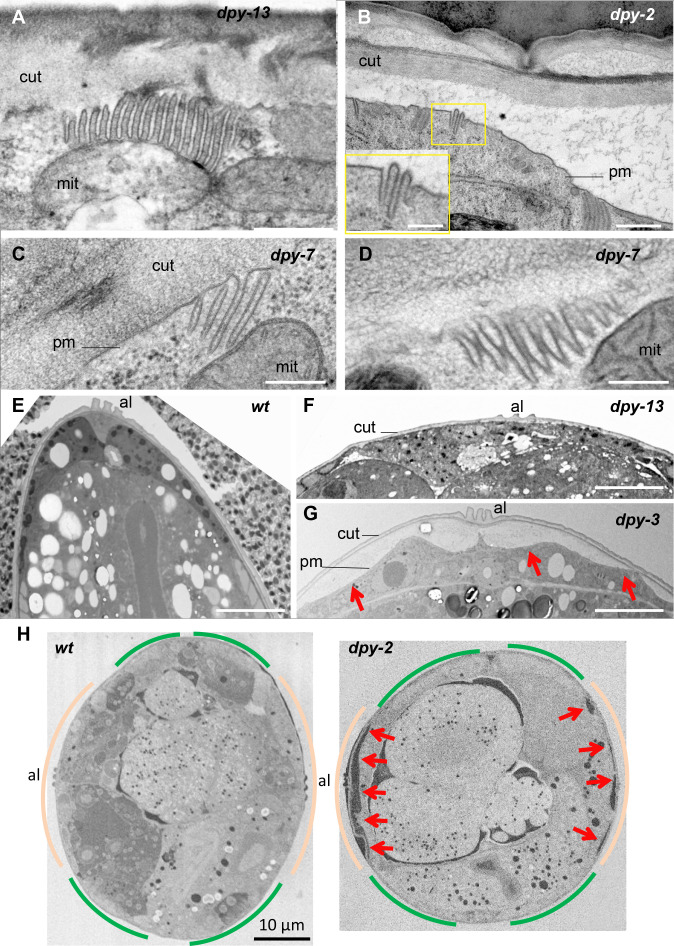
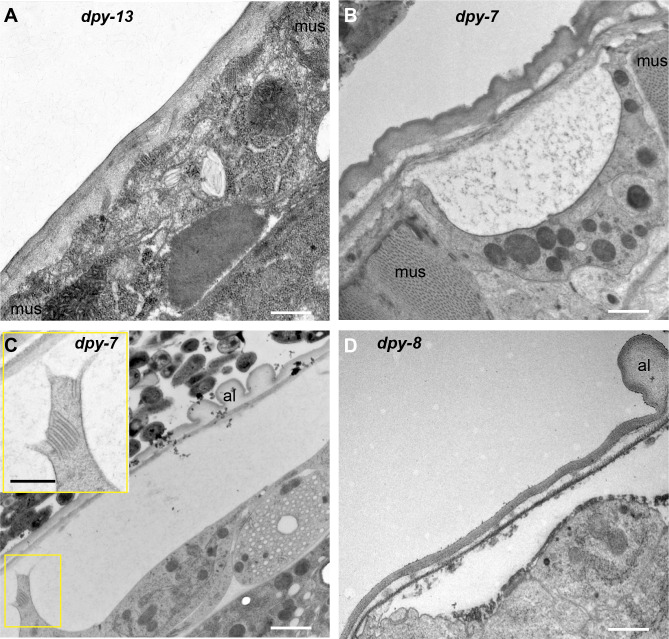
Figure 7. Furrow collagen inactivation leads to smaller and abnormal meisosomes and detachment of the cuticle.
TEM images of young adult worms. Compared to wild-type (Figure 1) or dpy-13 (A), dpy-2 (B) dpy-7 (C–, D) have abnormally small meisosomes with irregular spacing between the membrane folds (D); number of worms analysed are given in Table 1. Compared to wild-type (E) or dpy-13 (F), lower magnification reveals detachment of the cuticle (cut) from the plasma membrane (pm) in dpy-3 mutant worms over the whole lateral surface of the epidermal cell, on both sides of the alae (al) (G). (H) Compared to wild-type (left), serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) analysis of the entire transversal worm also reveals the detachment (red arrow) in a dpy-2 mutant of the cuticle from the lateral epidermis, contrary to the regions above the muscles, delineated in beige and green, respectively (one representative slice per animal, entire transversal sections were acquired over a length of 21.5 and 34.4 µm, for a wild-type and a dpy-2 mutant worm, respectively). Scale bar 500 nm in (A, B), 250 nm in inset in (B), 200 nm in (C, D), 5 µm in (E–G), and 10 µm in (H).