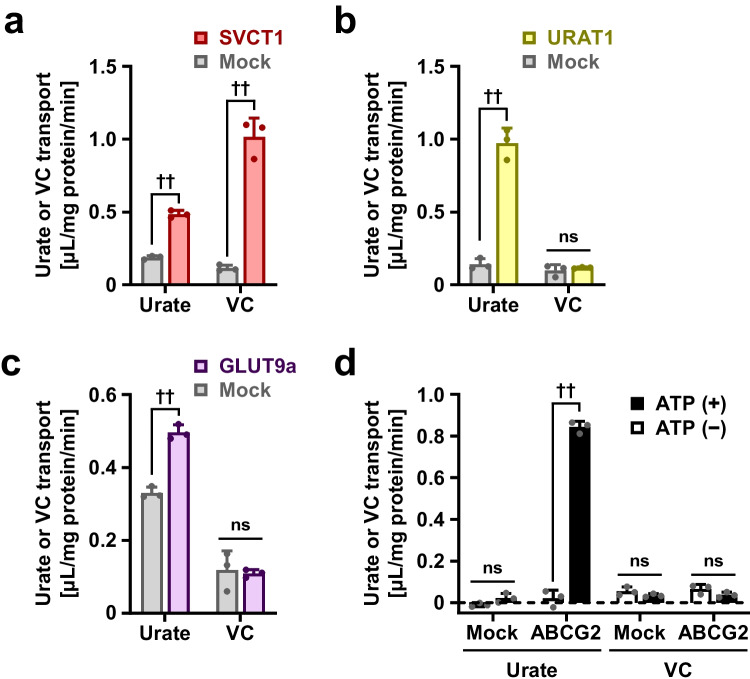
Fig. 2.
Investigation of vitamin C transport activities in physiologically important urate transporters. Regarding SVCT1 (a), URAT1 (b), GLUT9a (c), and ABCG2 (d), [8-14C]-urate or [1-14C]-vitamin C transport activities were investigated. SVCT1 exhibited a dual substrate specificity, whereas URTA1, GLUT9a, and ABCG2 lacked vitamin C transport activities. Cell-based uptake assays were conducted in Krebs–Ringer buffer (a), Cl−-free Hanks’ balanced salt solution (b), or high-potassium transport buffer (c); incubation time for uptake was 5 min. In vitro transport assay was carried out using ABCG2-expressing plasma membrane vesicles; incubation time for uptake was 10 min (d). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD; n = 3. ††P < 0.01; ns, not significantly different between groups (two-sided t-test)