Figure 3.
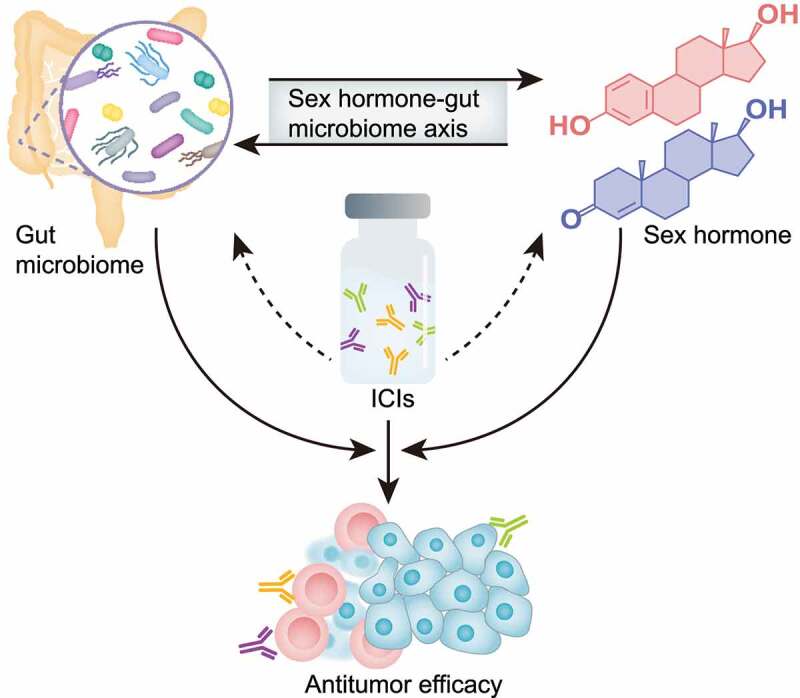
The role of the sex hormone-gut microbiome axis in tumor immunotherapy. Gut microbiome can influence the host’s levels of sex hormones through either metabolizing sex hormones or regulating gonadal secretion. In turn, the sex hormones can alter the gut microbiome by either serving as an energy source to support the growth of certain bacteria or regulating intestinal immune homeostasis. The interaction between sex hormones and gut microbiome constitutes the sex hormone-gut microbiome axis. Thus, the influences of gut microbiome and sex hormones on the patient’s response to ICIs can be simultaneously studied, although a growing body of evidence showed the effect of each of them on the antitumor efficacy of ICIs.
