Figure 1.
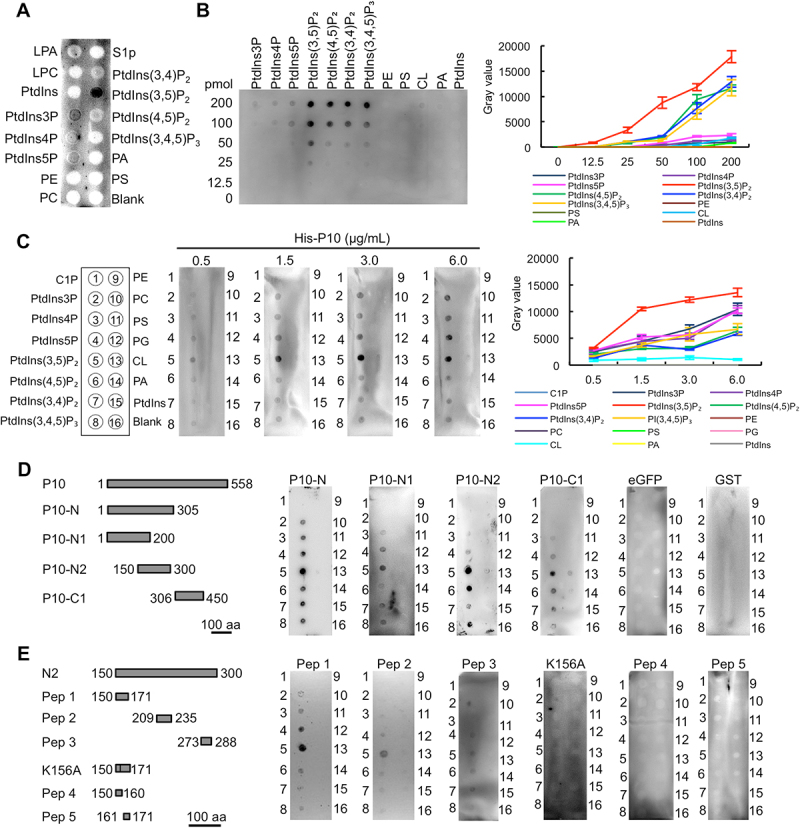
RBSDV P10 protein binds to PtdIns(3,5)P2. (A) The binding between RBSDV crude extract and phospholipids. (B) The binding between different phospholipids and P10 protein (1.5 μg/mL). (C) The binding between P10 protein at a gradient concentration and phospholipids. (D) The binding between P10 truncated proteins (50 μg/mL) and phospholipids. (E) The binding between P10 peptides (50 μg/mL) and phospholipids. The binding was analyzed by lipid binding assay. LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; C1P, ceramide-1-phosphate; PtdIns3P, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate; PtdIns4P, phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate; PtdIns5P, phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate; PtdIns(3,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,4)P2, phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PS, phosphatidylserine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; CL, cardiolipin; PA, phosphatidic acid; PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol.
