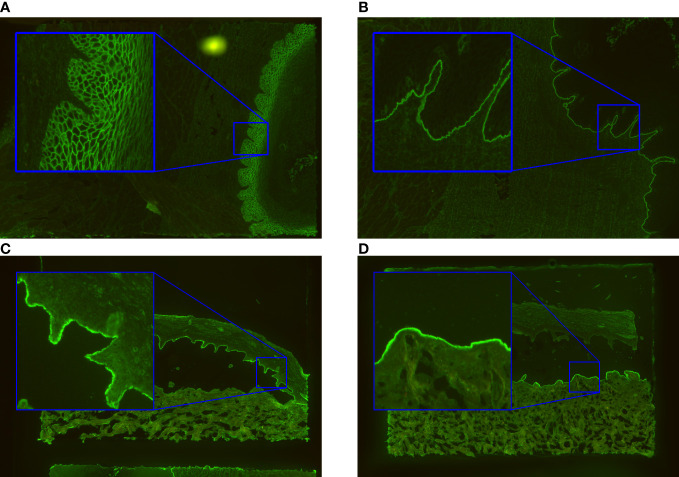
Figure 1.
Exemplary immunofluorescence images of the incubated substrates esophagus and salt-split skin. The ‘intercellular’ pattern seen by intercellular labelling of monkey esophagus in pemphigus vulgaris/foliaceus is shown in (A). In (B), the basal membrane zone (‘BMZ’) pattern typical for pemphigoid diseases is indicated. The patterns found in salt-split skin are ‘epidermal’ (C) and ‘dermal’ (D). They arise by binding of autoantibodies in pemphigoid patients to the epidermal or dermal side of the artificial split.