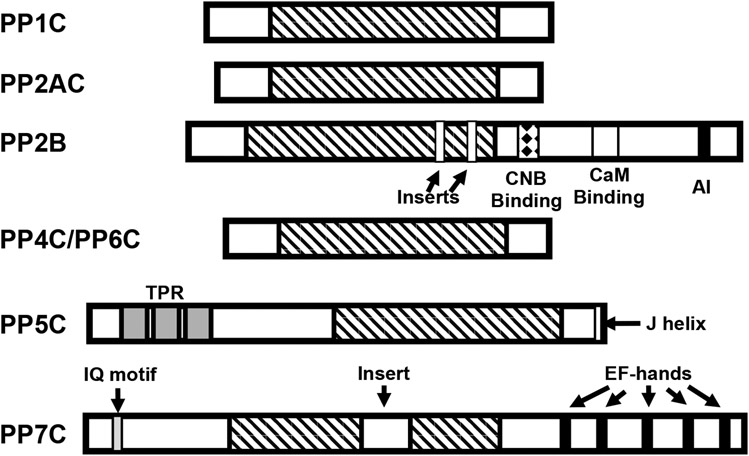
Figure 3. Homology and domain organization of PPP-family phosphatases.
PPPase share a highly conserved catalytic core domain of ~250 amino acids (indicated by diagnal stripes). PPP1, PPP2, PPP4, and PPP6 catalytic subunits are highly homologous enzymes, differing primarily in their C- and N-terminal regions. PP2B catalytic subunits (calcineurin A) differs in that it has a large C-terminal extension containing a regulatory subunit (calcineurin B; CNB) binding site (indicated by a diamond filled box), a Ca2+-calmodulin (CaM) binding domain (indicated by a white box), a short autoinhibitory (AI) domain in its C-terminal region and two small divergent regions (inserts) in the catalytic core. PPP5C possesses three tetratricopeptide repeats (TPRs - indicated by grey boxes) in its N-terminal region and a short regulatory helix (J helix; indicated by a white box) at its C-terminus. PPP7 contains a CaM binding IQ motif (gray box) in its N-terminal region, Ca2+ binding EF-hand motifs (indicated by black boxes) in its C-terminal region and a 43-amino acid insert in the catalytic core domain (indicated by an open box).