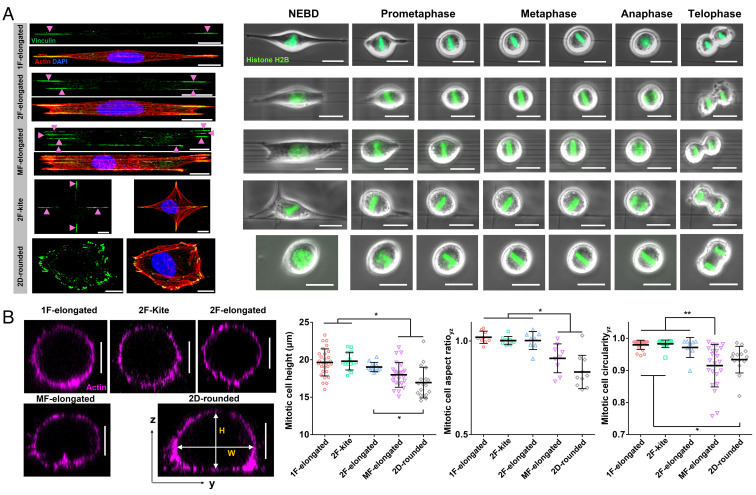
Fig. 1.
Cell division in suspended fiber environments. (A) Time-lapse images showing representative cases of mitotic progression starting from nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD) to telophase corresponding to five distinct interphase cell shapes: 1F-elongated, 2F-elongated, MF-elongated (≥3 fibers), 2F-kite (2 orthogonal fibers), and 2D-rounded (glass coverslips). Interphase cells are fluorescently stained with actin (red), vinculin (green), and nucleus (blue). (Scale bars, 10 µm and 20 µm, respectively.) (B) Representative yz cross-sectional images of actin-stained cells fixed at metaphase for different substrate categories, mitotic cell height (H), mitotic cell AR (H/W), and mitotic cell circularity (4*π*area/perimeter2) for different substrate categories. No statistical differences were observed between 1F-elongated, 2F-kite and 2F-elongated categories in terms of mitotic cell height, AR and circularity. (Scale bar, 10 µm.) *, **, ***, and **** represent P < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001, and 0.0001, respectively.