FIGURE 4.
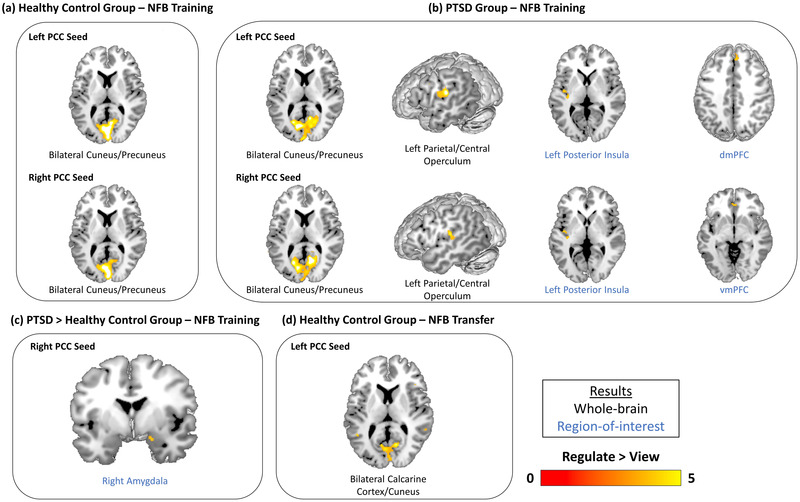
Within‐ and between‐group differences in functional connectivity of the PCC during the 3 neurofeedback training runs and the transfer run. Results show brain areas that were found to display increased functional connectivity with the PPI seed region (left or right PCC) during regulate as compared to view conditions. (a) The within‐healthy control group comparison revealed left and right PCC connectivity with the bilateral cuneus/precuneus during regulate as compared to view conditions for the neurofeedback training runs. (b) The within‐PTSD group comparison revealed left and right PCC connectivity with the bilateral cuneus/precuneus, left parietal/central operculum, and left posterior insula during regulate as compared to view conditions for the neurofeedback training runs. Additionally, left PCC‐dmPFC and right PCC‐vmPFC connectivity was also observed during regulate as compared to view conditions for the neurofeedback training runs. (c) The between‐group comparison revealed that the PTSD group displayed increased right PCC‐right amygdala connectivity relative to the healthy control group during regulate as compared to view conditions for the neurofeedback training runs. (d) The within‐healthy control group comparison revealed left PCC connectivity with the bilateral calcarine cortex/cuneus during regulate as compared to view conditions for the neurofeedback transfer run. All results are evaluated at the FWE‐peak corrected threshold for multiple comparisons (p < .05, k = 10). NFB = neurofeedback, PCC = posterior cingulate cortex, dmPFC = dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, vmPFC = ventromedial prefrontal cortex.
