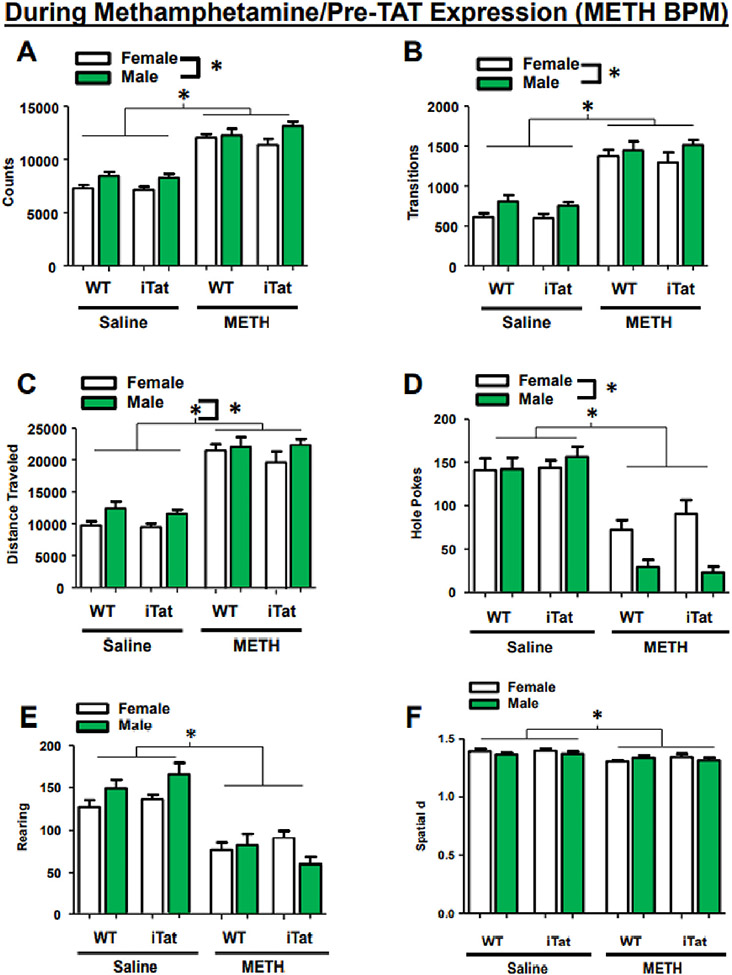
Fig. 3.
Previous exposure to METH alters activity in the BPM. Mice previously exposed to METH exhibited higher total behavioral activity (A), transitions (B), and travel distance (C), with all males showing higher scores compared to females across all groups. METH exposure also reduced holepoking behavior (D), rearing (E), and spatial d (F). Holepoking behavior showed a sex × drug interaction, with male mice performing significantly lower than female mice (D). Data presented as mean ± SEM. * = p < 0.05.