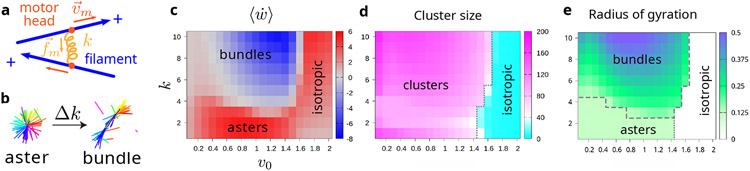
FIG. 1.
Structural transition between asters and bundles. (a) Schematic of two filaments (blue) connected by a motor (orange). The motor is modeled as a Hookean spring with rigidity k. The motor force is proportional to motor rigidity k. Each motor head (dark orange) binds to one filament and moves towards the barbed (+) end with velocity (Eq. (1)). When the motor is bound to two filaments, the rate of work done by the motor spring is computed as the sum of over the two motor heads. (b) Tuning k induces the structural transition between asters and bundles. (c) Color map of . Asters and bundles are respectively associated with positive and negative values of . (d) Color map of the largest cluster size. A system with no cluster larger than 40 is considered to be isotropic. (e) Color map of radius of gyration Rg of the largest cluster. The boundary between bundle and aster is Rg = 0.125. The boundary of isotropic is the same as in (d).