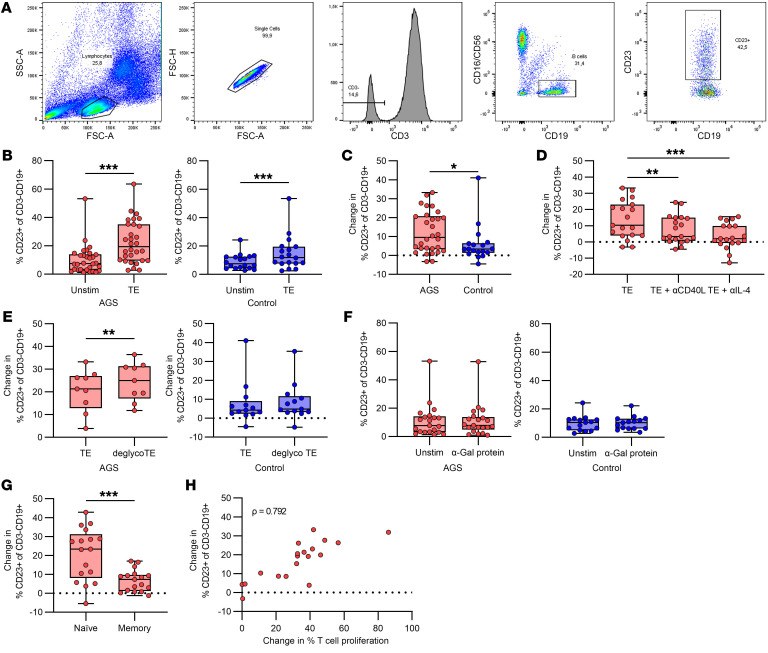
Figure 4. B cell expression of CD23.
(A) Gating strategy for CD23-expressing B cells. (B) CD23 expression in unstimulated compared with TE stimulated B cells in patients with AGS (left, n = 30) and healthy controls (right, n = 18), Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, ***P < 0.001. (C) Comparison of patients with AGS and healthy controls, Mann-Whitney U test, *P < 0.05, n = 30 (AGS) and n = 18 (controls). (D) Effect of inhibition with anti-CD40L and anti-IL-4 antibodies in patients with AGS, Friedman test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n = 19. (E) Effect of removing α-Gal from the TE in patients with AGS (left, n = 9), and healthy controls (right, n = 13), Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, **P < 0.01. (F) Comparison of CD23 expression in unstimulated B cells compared with B cells stimulated with an α-Gal containing nontick protein in patients with AGS (left, n = 21) and healthy controls (right, n = 15). (G) Comparison of CD23 expression by naive (CD27-IgD+) and memory (CD27+) B cells after TE stimulation in patients with AGS, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, ***P < 0.001, n = 17. Each point within the box plot represents 1 individual. Box plots represent IQR and median, whiskers extend to the farthest data points. (H) Correlation of T cell proliferation and CD23 expression in response to TE in patients with AGS, Spearman’s rank correlation, ρ = 0.792, P < 0.001, n = 19. Each point represents 1 individual.