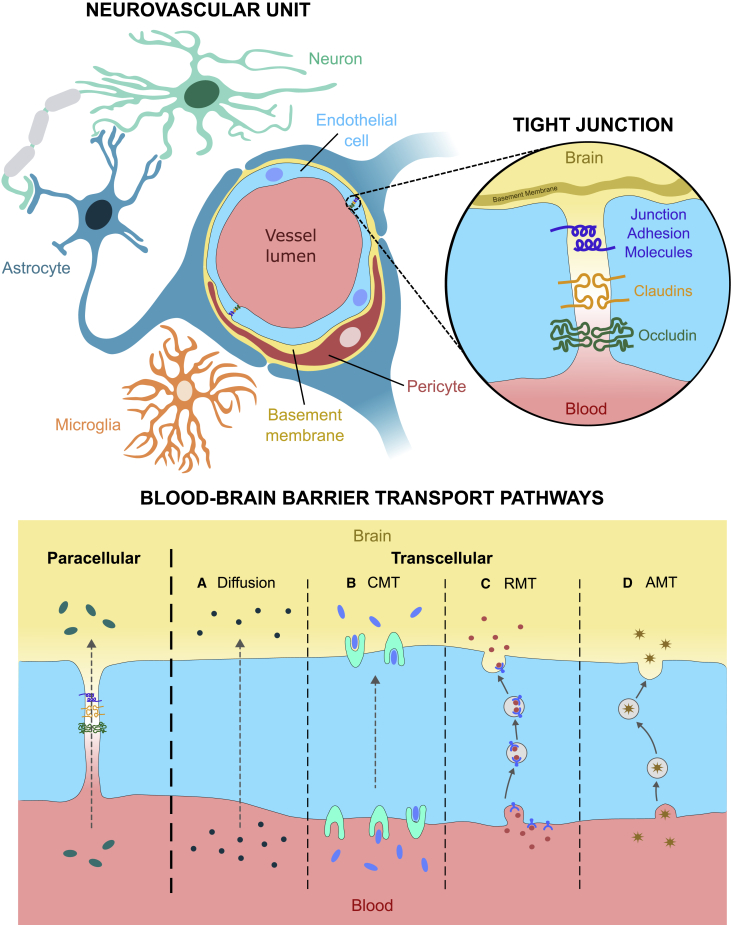
Figure 1.
The neurovascular unit and blood-brain barrier transport pathways
Graphical depiction of the neurovascular unit (NVU), the fundamental anatomical and functional unit of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), including the key protein components of tight junctions (TJs) between brain endothelial cells which control the paracellular transport pathway. Alternatively, molecules may be transported transcellularly via passive diffusion (A), carrier-mediated transcytosis (CMT) (B), receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) (C), or adsorptive-mediated transcytosis (AMT) (D).