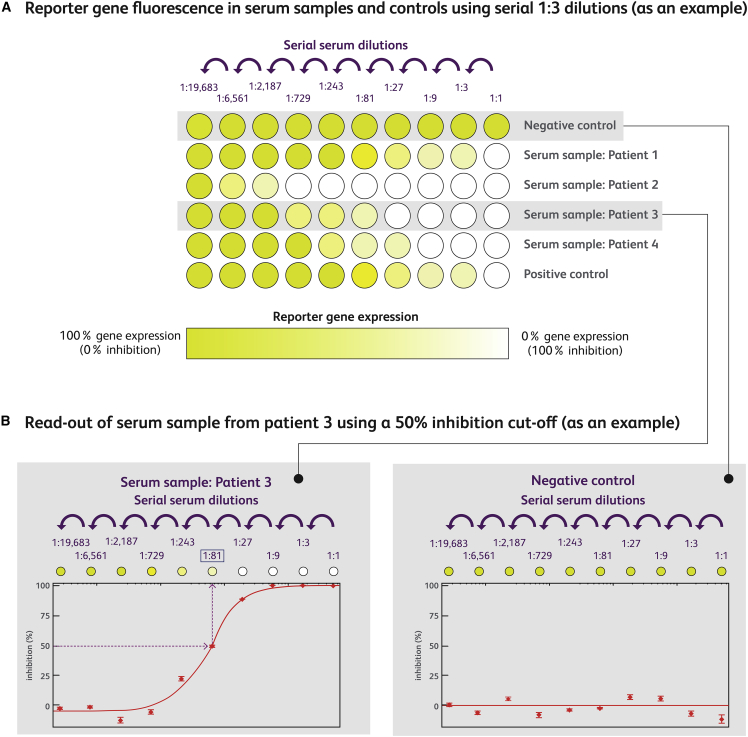
Figure 4.
Readout of a semi-quantitative transduction inhibition assay
These principles also apply to total antibody assay. (A) Reporter gene expression in serial one in three dilutions of serum samples of four patients and positive and negative controls. The negative control does not contain neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies (or non-antibody neutralizing factors); therefore, the rAAV vector transduces the target cells where the reporter gene is expressed (yellow well). The positive control contains neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies, often marginally above the screening titer cutoff. Patient serum samples one to four contain varying levels of neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies (or non-antibody neutralizing factors) that affect the level of reporter gene expression seen at different dilutions. (B) The degree of inhibition of reporter gene expression is plotted against the dilutions of the serum sample.48,49,56 The 50% inhibition cutoff from the resulting curves is based on the highest sample dilution that achieves 50% inhibition of vector transduction in comparison with the negative-control sample. In this example, patient 3 has an anti-AAV NAb titer of 1:81, which will be compared with the screening titer cutoff to determine patient eligibility. If the patient 3 titer of 1:81 ≥ screening titer cutoff (e.g., 1:3), the patient would be ineligible for the rAAV GTx. AAV, adeno-associated virus; rAAV, recombinant AAV; TAb, total antibody; TI, transduction inhibition.