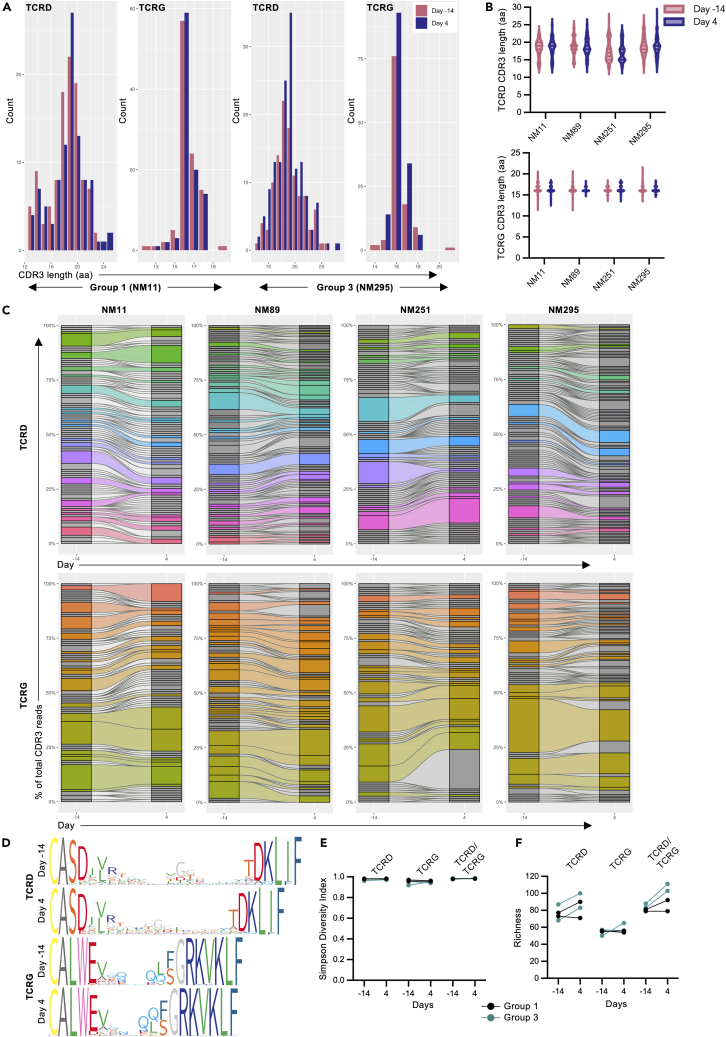
Figure 7.
Clonality of in-vivo-expanded Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in pigtail macaques
Clonality was assessed by paired gamma and delta chain sequencing from peripheral blood Vγ9Vδ2 T cells pre-expansion (day 14) and during peak expansion (day 4) (n = 4 animals from 1 experiment).
(A) Representative TCRD and TCRG CDR3 amino acid length distributions in peripheral blood Vγ9Vδ2 T cells from a group 1 animal (NM11) and a group 3 animal (NM295).
(B) TCRD and TCRG CDR3 amino acid length distributions across all 4 PTMs pre-expansion (day 14, red) and during peak expansion (day 4, purple).
(C) TCRD and TCRG clonal diversity and clonotype sharing within each individual animal pre-expansion and during peak expansion. Gray bar segments represent individual clonotypes that were identified at 1 timepoint, while colored segments illustrate clonotypes that were shared between both timepoints.
(D) Sequence logos generated from all TCRD or TCRG CDR3 amino acid sequences from 1 animal (ClustalW alignment algorithm). Narrower bars in the logos represent gaps in the sequence. Individual amino acids are colored according to the RasMol amino color scheme.
(E) Simpson diversity index for Vγ9Vδ2 T cell TCRD, TCRG, and paired TCRD/TCRG clonotypes.
(F) Unique clonotype frequencies (richness) for Vγ9Vδ2 T cell TCRD, TCRG, and combined TCRD/TCRG chains. Individual points on the graphs represent an individual animal at each timepoint. p values for diversity and richness changes are presented in Table S1, and additional sequencing data are presented in Figure S6.