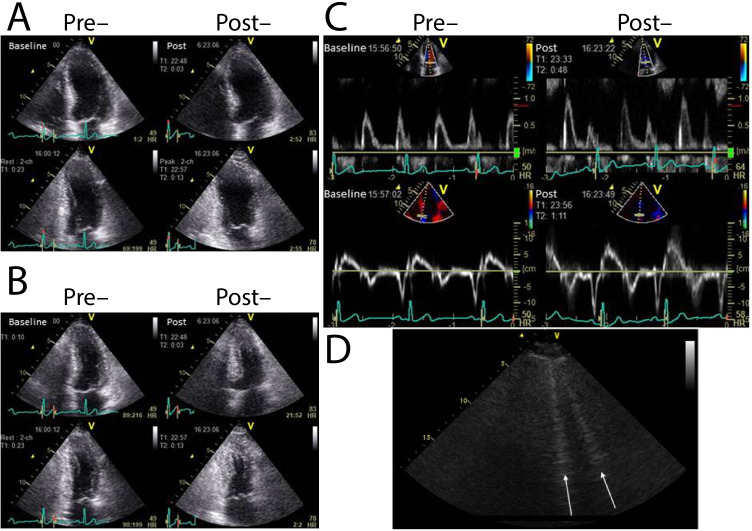
Fig. 4.
Echocardiography prior to and post exercise can reveal comparatively subtle increases in diastolic dysfunction. Reproduced here is the case of a 75-year-old male with current exertional dyspnoea and a history of percutaneous coronary interventional therapy. Wall motion analysis revealed no exercise-induced wall motion abnormality in either view (A, B). The measured mitral flow pattern and tissue Doppler was consistent with that of delayed relaxation (C) and E/E’ increased from 14 at rest to 16 with exercise [127]. Similarly, hyperechoic b-lines that arise in the lung from transudated fluid (D) that can be detected in HFpEF patients with dyspnoea, with good prognostic power [128]