Figure 3.
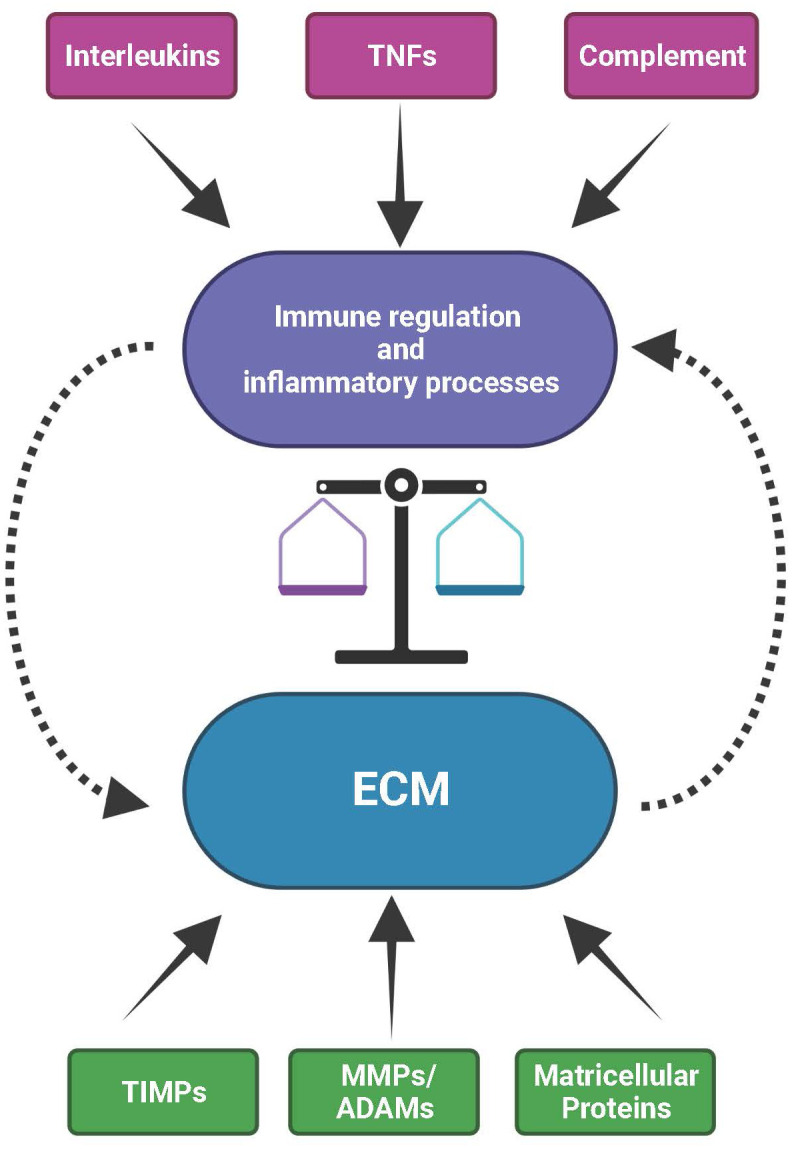
The mutual interplay between the extracellular matrix (ECM) and immunological processes. The ECM with its structural constituents but also its functional components, such as ECM remodeling enzymes (MMPs, ADAMs and TIMPs) and matricellular proteins, provides the microenvironment for the activity of immune and inflammatory processes. Vice versa, immunological/inflammatory activities contributed by e.g., interleukins, tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) or complement can influence the structural and functional organization of the ECM. As a consequence, disturbances in the expression or activity of factors that are part of the ECM or of the immune system affect the balance between inflammatory events and ECM homeostasis. These can eventually impact natural ageing, environmental insult or high genetic risk, together eventually initiating and sustaining onset and progression of progressive disease processes in the retina.
