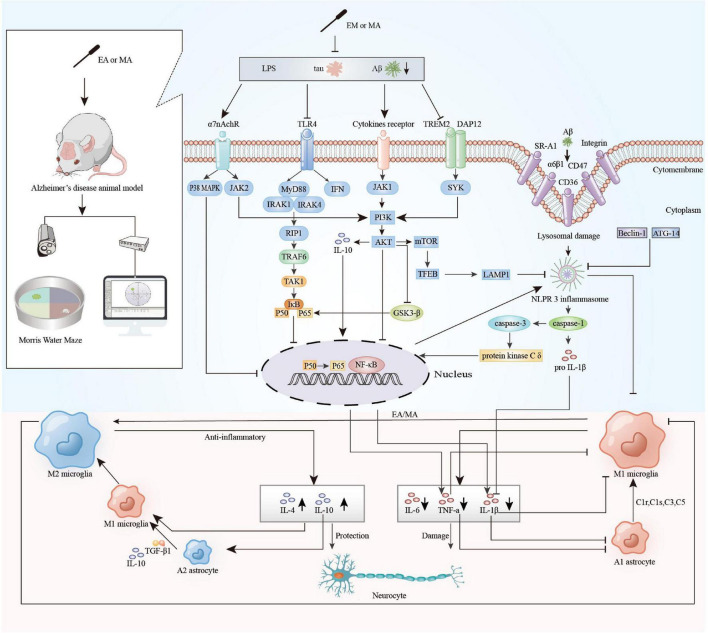
FIGURE 6.
The main mechanisms of acupuncture to regulate neuroinflammation in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). EA, electroacupuncture; MA, manual acupuncture; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Tau, microtubule-associated protein tau; Aβ, beta-amyloid; α7nAChR, alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; TLR4, toll-Like receptor 4; TREM2, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2; DAP12, DNAX-activating protein 12; SR-A1, scavenger receptor A1; α6β1, integrin α6β1; P38 MAPK, P38 mitogen activated protein kinases; JAK2, janus kinase 2; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; IFN, interferon; JAK1, janus kinase 1; SYK, spleen tyrosine kinase; IRAK1, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase1; IRAK4, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; RIP1, receptor-interacting protein 1; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; TAK1, transforming growth factor β activated kinase 1; Iκβ, inhibitor κB kinase β; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-B; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; TFEB, transcription factor EB; LAMP, lysosome-associated membrane protein 1; ATG-14, autophagy protein 14; Beclin 1, autophagic protein Beclin 1; NLRP3 inflammasome, nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; C1r, complement 1r; C1s, complement 1s; C3, complement 3; C5, complement 5; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-a; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-4, interleukin 4; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-10, interleukin 10.