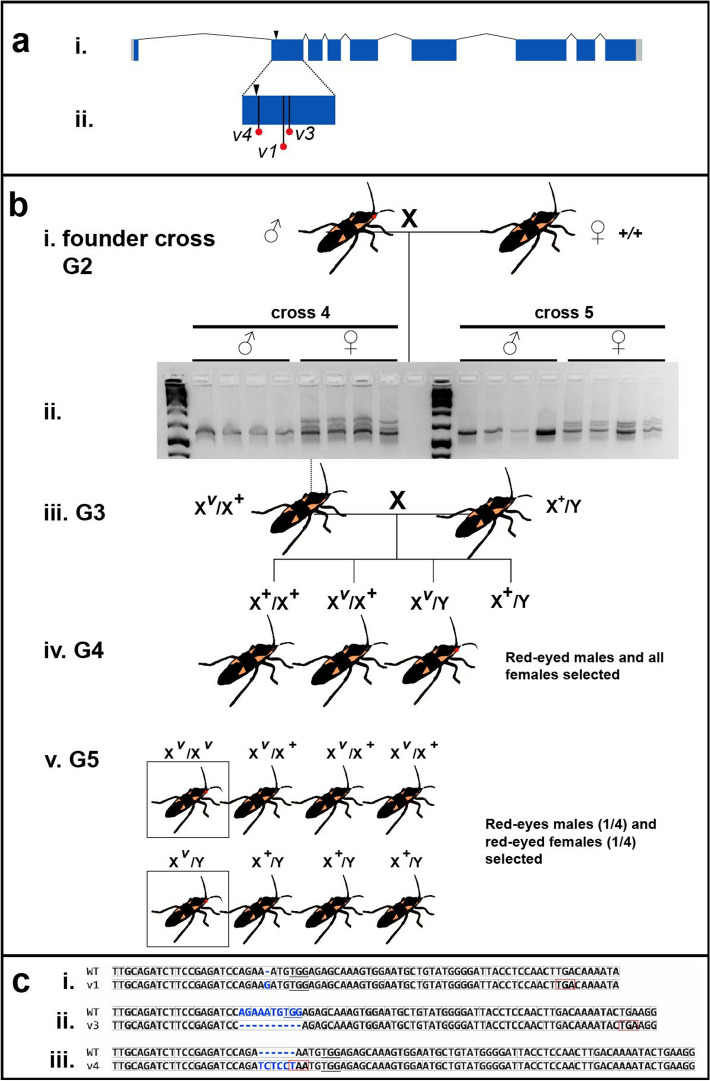
Figure 3.
Generation of Of-v mutant lines using CRISPR/Cas9. (A) An Of-v gRNA was designed to guide Cas9 to generate a double-stranded break (arrowhead) in Of-v exon 2. (i) Of-v gene structure, with coding DNA sequence shown in dark blue and untranslated regions shown in light gray. (ii) Premature stop codons found in exon 2 of all mutant alleles. (B) Crossing scheme to generate homozygous lines from a heteroallelic Of-v mutant stock. (i) Five single crosses were set up between a single red-eyed Of-v G2 male founder (derived from the heteroallelic Of-v population) and three wild-type virgin females. (ii) Of-v exon 2 was amplified from genomic DNA isolated from the progeny of these crosses and a heteroduplex mobility assay performed; all females gave rise to heteroduplex bands, while no heteroduplex bands were found in male samples, consistent with Of-v X linkage; (iii) One G3 female offspring from each founder cross was mated with one or more wild type males; (iv) Male G4 offspring had either red or black eyes, while all female G4s had black eyes. All red-eyed males were selected to mate with female siblings; (v) In the G5, all red-eyed males and red-eyed virgin females were selected to establish homozygous lines. The expected genotypes and phenotypes are shown in their expected proportions. (C) Alignment between the wild-type Of-v allele and the three mutant alleles for which homozygous lines were successfully established: (i) v1, single nucleotide insertion at the predicted double-stranded break site; (ii) v3, 10 bp deletion; (iii) v4, 6 bp insertion. Insertions or deletions, blue. Reading frame, light gray boxes. Introduced stop codons, red boxes. PAM site, underline.