Figure 5. Hmcn1 and Nid2a proteins display partially overlapping localization at basement membranes of zebrafish embryos.
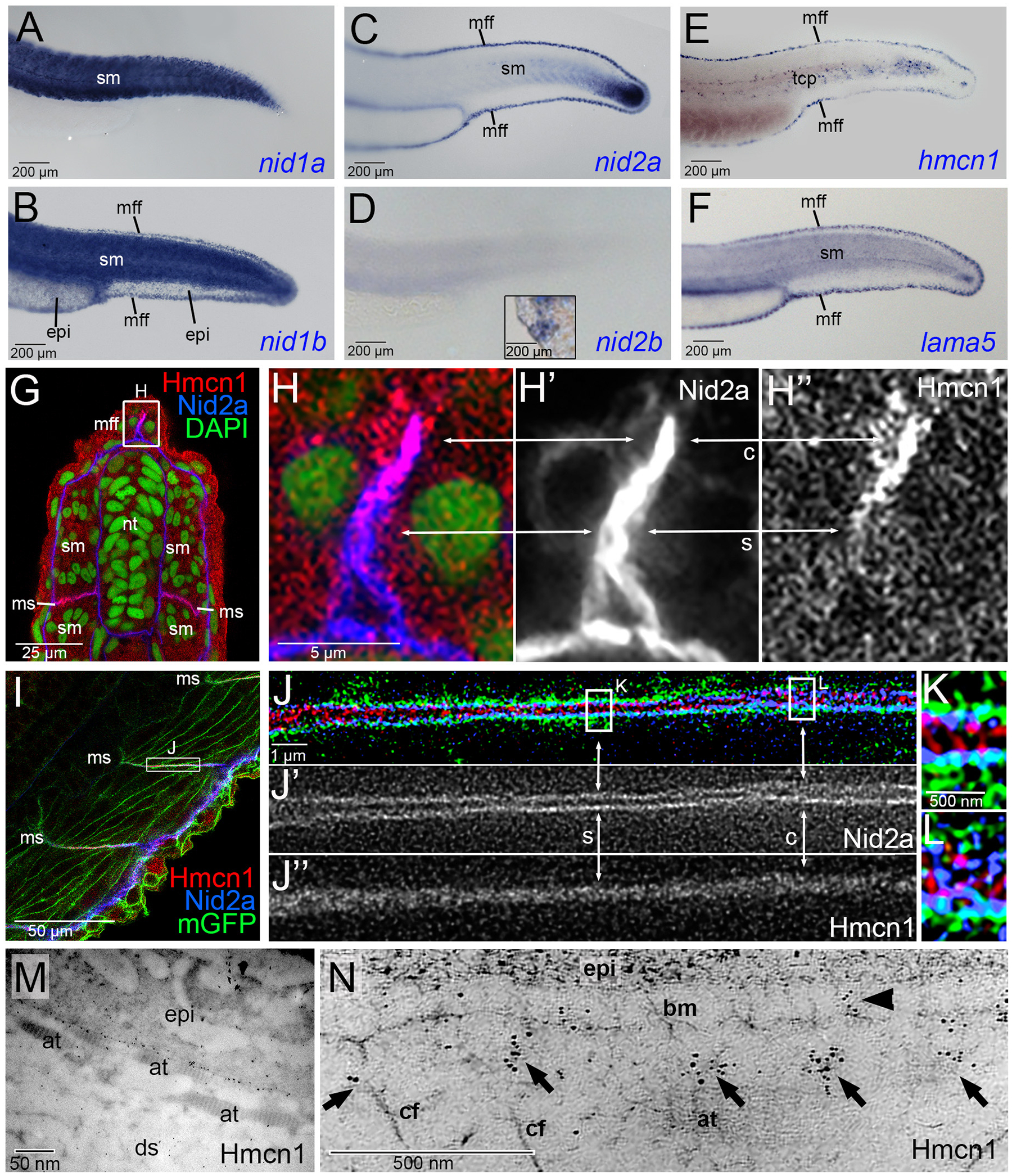
(A-F) Lateral views of tails of zebrafish embryos at 30 hpf, stained via whole mount in situ hybridization for nid1a, nid1b, nid2a, nid2b, hmcn1 or lama5 transcripts. hmcn1 and nid2a as well as lama5 are co-expressed in epidermal cells of the median fin fold and in somitic muscle cells. Note the expression of hmcn1 transcript in tenocyte precursor cells (tcp, E). Inset in D shows labelling of hatching gland cells of same embryo, serving as a positive nid2b control. (G-L) Immunofluorescence analysis of developing dermal-epidermal (G-H”) and myotendinous junctions (I-L) of 24 hpf zebrafish, using antibodies directed against Hmcn1 (red) and Nid2 (blue), and counterstained with DAPI (green) to label nuclei (G,H) or with an antibody against Tg(Ola.Actb:Hsa.hras-egfp)-encoded GFP to label cell membranes (I-K). (H-H”) shows higher magnification of the apical region of dorsal median fin fold boxed in G, (J-J”) shows higher magnification of myotendinous junction region boxed in (I), and (K,L) further magnifications of regions boxed in (J). (G,H,I,J,K,L) show merged channels, (H’,J’) Nid2a single channels and (H”,J”) Hmcn1 single channels. (H-H”) Higher magnification of the median fin fold shows Hmcn1 localization largely co-localized with Nid2a in distal, developmentally less advanced regions (50) of the fin fold (arrows labelled with “c”). In comparison, in proximal, developmentally more advanced regions, Hmcn1 and Nid2 localization have started to segregate (arrows labelled with “s”). (J-J”) Higher magnification of the mytendinous junction between two myosepta using STED microscopy shows Hmcn1 localization largely separated (indicated by arrows labelled with “s” in J and magnified in K) or co-localized (indicated by arrows labelled with “c” in J and magnified in L) with Nid2a protein. (M) Overview of ultrastructural immunolocalization of Hmcn1 at dermal-epidermal junction of median fin fold of 54 hpf embryo. (N) Higher magnification reveals clusters of Hmcn1 signals distributed underneath (arrows) or even within (arrowhead) the skin BM. Abbreviations: at, actinotrichia; bm, basement membrane; c, co-localized; cf, cross fibers; ds, dermal space; epi, epidermis; mGFP, cell membrane-associated GFP; mff, median fin fold; ms, myoseptum; s, separated; sm, somitic muscle; tcp, tenocyte precursors.
