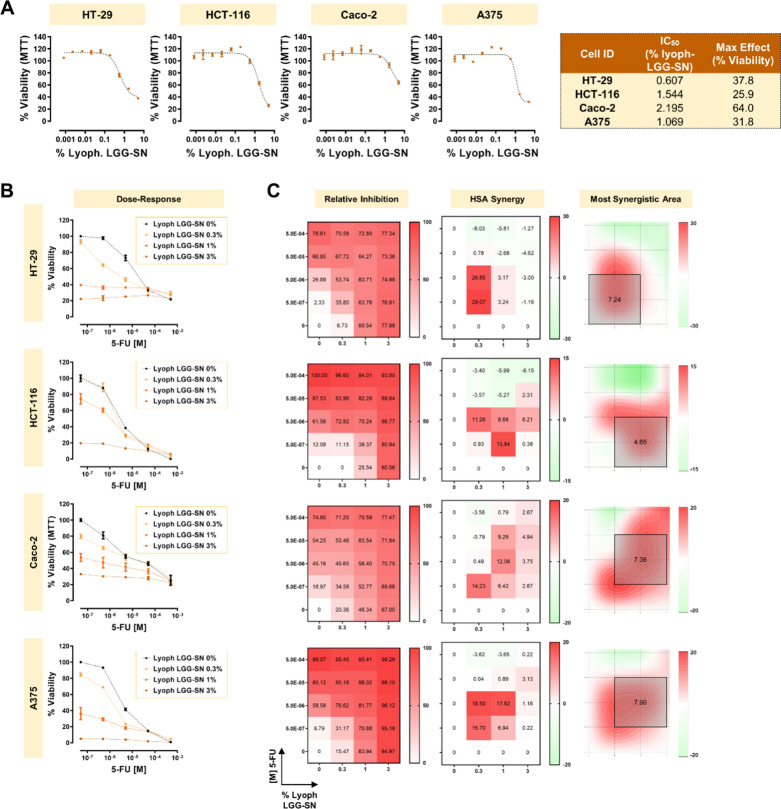
Fig. 6.
Lyophilized cell-free LGG-SN (Lyoph-LGG-SN) selectively reduces the viability of cancer cells in a concentration-dependent manner, and it shows a synergistic effect in combination with 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU). A. Concentration–response plots for HT-29, HCT-116, Caco-2, A375 treated with increasing concentrations of Lyoph-LGG-SN (up to 5% v/v). MTT assay readout reveals a concentration dependent decrease of cellular viability in the four cancer cell lines. Table on the right summarizes the IC50 (% of Lyoph-LGG-SN, v/v) and maximum effect (% viability) calculated per each cell line. B. HT-29, HCT-116, Caco-2, A375 concentration response plots. Cells treated with 5-FU (from 5.0 × 10–7 M to 5.0 × 10–4 M) in combination with different concentrations of Lyoph-LGG-SN (0.3%, 1% and 3% v/v). C. HT-29, HCT-116, Caco-2, A375 relative inhibition matrices (left), Highest Single Agent (HSA) synergy matrices (middle), synergy surface with most synergistic area (black square, with corresponding HSA synergy score). N = 3. Values are presented as Mean ± SD