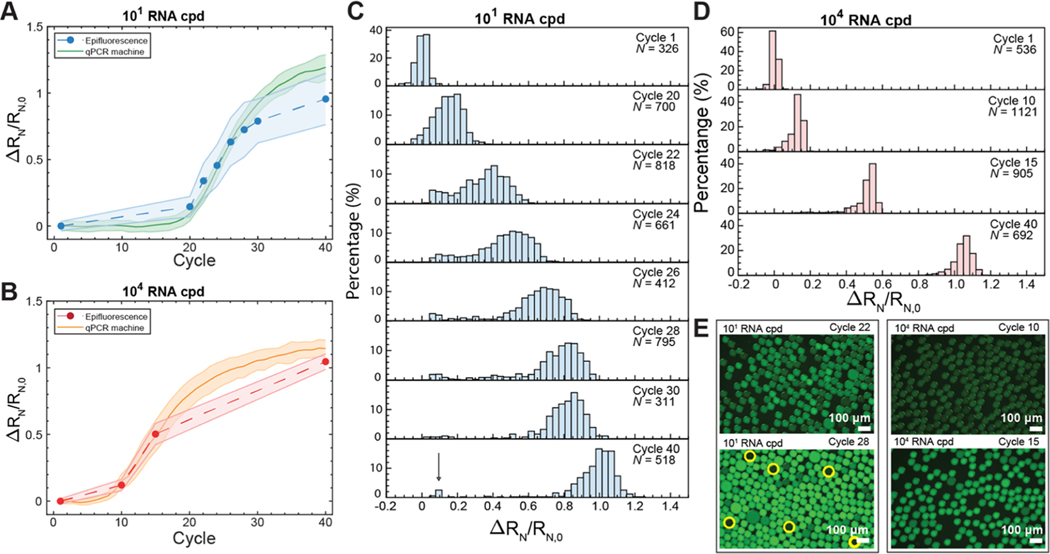
Figure 4.
OCD RT-qPCR amplification curves compared to standard qPCR curves. Drops containing (A) 1.71 × 101 cpd of M gene RNA (low). The solid green line represents real-time pseudocontinuous fluorescence measurements of drops at each cycle using qPCR. The blue-dashed line follows fluorescence measurements of sampled individual drops. Shaded error bars represent one standard deviation. Drops containing (B) 1.71 × 104 cpd of M gene RNA (high). The solid orange line represents pseudocontinuous fluorescence measurements of drops at each cycle using qPCR. The red-dashed line follows fluorescence measurements of sampled individual drops. (C) Histograms of individual drop fluorescence values from epifluorescence images for 1.71 × 101 cpd of M gene (low). N represents the number of drops measured. The arrow in cycle 40 indicates unamplified drops. (D) Histograms of individual drop fluorescence values from epifluorescence images for 1.71 × 104 cpd of M gene RNA (high). (E) Changes in fluorescence are observed from 1.71 × 101 or 104 cpd of M gene RNA at cycles 22 and 28 and cycles 10 and 15, respectively. Yellow circles indicate dark drops containing no template at cycle 28.