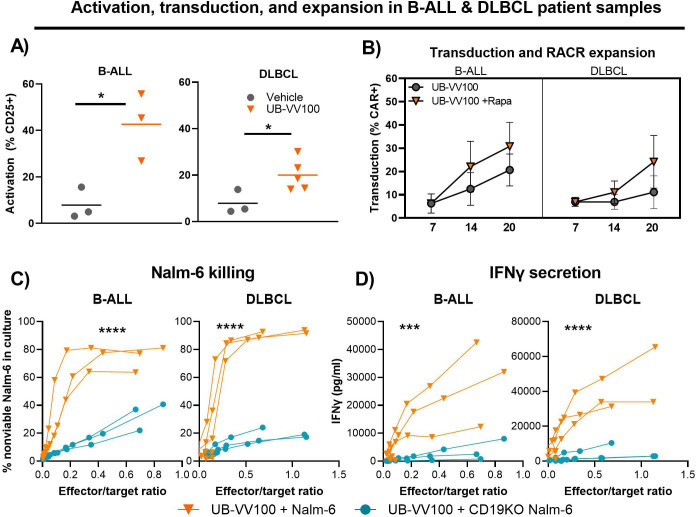
Figure 4.
UB-VV100 transduces functional CAR T cells from patient samples. In two separate experiments, PBMCs from patients with B-ALL and DLBCL were transduced with UB-VV100 at MOI of 5. (A) On day 3, the frequencies of T cells expressing CD25 were assessed in B-ALL and DLBCL samples. On day 7 post UB-VV100 transduction, cells were further cultured in the absence or presence of 10 nM rapamycin. *P<0.05, Student’s t-test. Bars indicate mean. (B) The frequencies of CAR T cells on days 7, 14, and 20 were determined by flow cytometry. On day 20, rapamycin-expanded CAR T cells from B-ALL and DLBCL patient samples were cocultured with Nalm-6 or CD19KO Nalm-6 tumor cells. (C) After 24 hours of coculture, the frequency of non-viable Nalm-6 tumor targets was determined by viability dye staining via flow cytometry. ****P<0.001, two-way ANOVA, main effect analysis for Nalm-6 identity. (D) The concentration of IFN-γ in the coculture supernatant was also measured in both B-ALL and DLBCL samples. Data points indicate mean±1 SEM. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, two-way ANOVA, main effect analysis for Nalm-6 identity. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; MOI, multiplicity of infection.