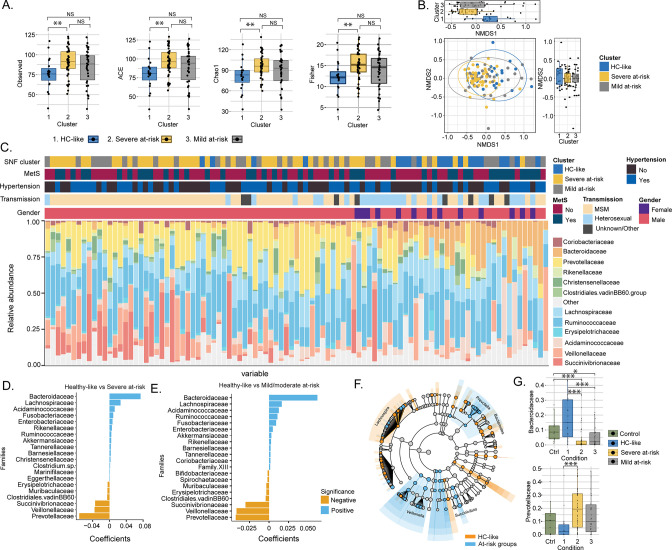
Figure 3. Transmission mode drove cluster differences in microbiome data.
(A) Boxplots of alpha diversity indices (Observed, ACE, Chao1, Fisher) separated by HIV cluster. Significant stars are shown for each comparison (Mann-Whitney U test). (B) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plot of Bray-Curtis distances. Samples are colored by clusters. Boxplots based on NMDS1 and NMDS2 are represented. (C) Barplot represents the relative abundance of bacteria at the family level for each patient. Patient information is displayed above the barplot, including cluster, metabolic syndrome (MetS: yes/no), hypertension (yes/no), transmission mode, and gender. (D) Barplot showing the top microbial families by representing their coefficient from PERMANOVA between SNF-1 and SNF-2. (E) Barplot showing the top microbial families between SNF-1 and SNF-3. (F) LEfSe cladogram representing cluster-specific microbial communities to HC-like and to at-risk groups (SNF-2/SNF-3). Top families from PERMANOVA are labeled. (G) Boxplot of relative abundance at family level for Bacteroides (top) and Prevotella (bottom). Significant stars are shown for significant comparisons (Mann-Whitney U test).