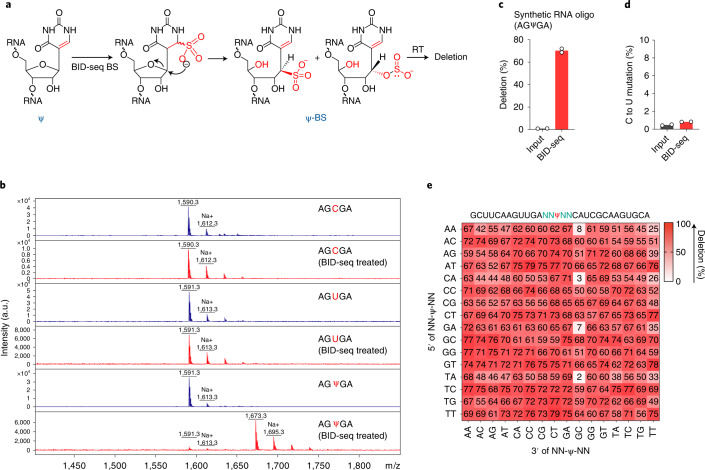
Fig. 1. BID-seq quantitatively detects Ψ sites as deletion signatures.
a, Chemical structure of the Ψ-BS adduct after bisulfite treatment. b, BID-seq BS selectively reacts with Ψ and completely converts it into the Ψ-BS adduct under optimized conditions, without affecting normal C or U bases in RNA. c, The deletion ratio at the 100% modified Ψ site within the AGΨGA motif (synthesized RNA oligo) after BID-seq treatment versus that in the input. d, The average C to U mutation ratio at normal cytidine bases in synthesized RNA oligo after BID-seq treatment versus that in input. For c–d, n = 2 biologically independent samples. e, Heatmap plot for deletion ratios on 256 motifs (NNΨNN) after BS treatment in BID-seq, which contain one 100% modified Ψ within each motif.