Fig. 2. Huc forms an 833-kDa oligomer comprising HucS, HucL and HucM.
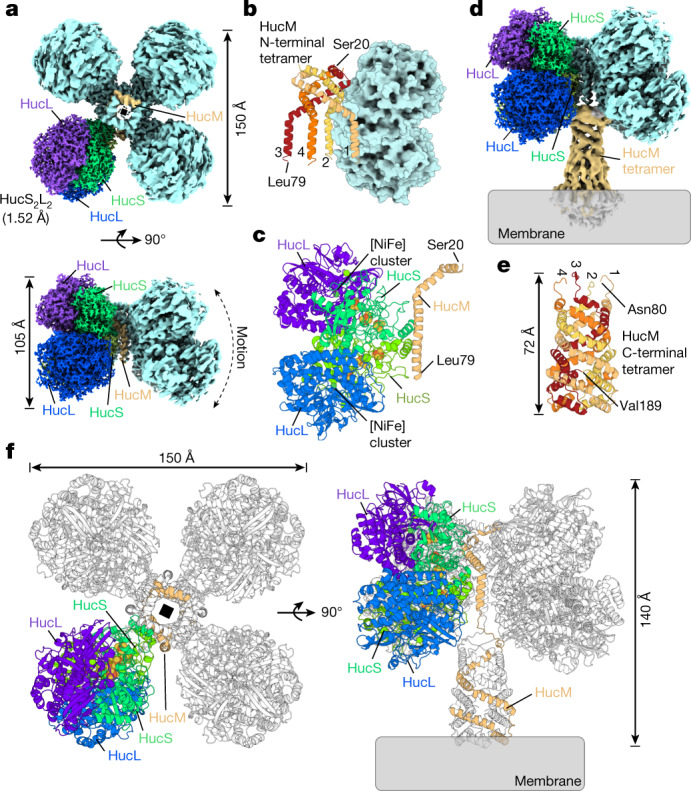
a, Cryo-EM density maps of the Huc oligomer showing its four lobes that each contain two HucSL dimers, with four centrally located HucM subunits acting as a scaffold for the oligomer. One lobe of Huc shows the 1.52 Å high-resolution map, with HucL and HucS subunits coloured individually as indicated. One HucM molecule is coloured orange. b, A cartoon representation of the central tetramer formed by 4 HucM subunits (residues 20 to 79), with a single HucS2L2 lobe shown as a surface model for context. c, A cartoon representation of the asymmetric unit of the Huc oligomer. d, A composite cryo-EM density map showing the Huc ‘body’ region as in a, and the ‘stalk’ region that is peripherally associated with the cell membrane. e, A cartoon representation of the AlphaFold2 model of the C-terminal region of HucM (residues 80 to 189), showing that it forms a tetrameric coiled-coil tube. f, A cartoon representation showing the full Huc complex reconstructed from the cryo-EM structure and AlphaFold model of the HucM C-terminal fitted to the cryo-EM density map of the stalk region.
