Figure 2.
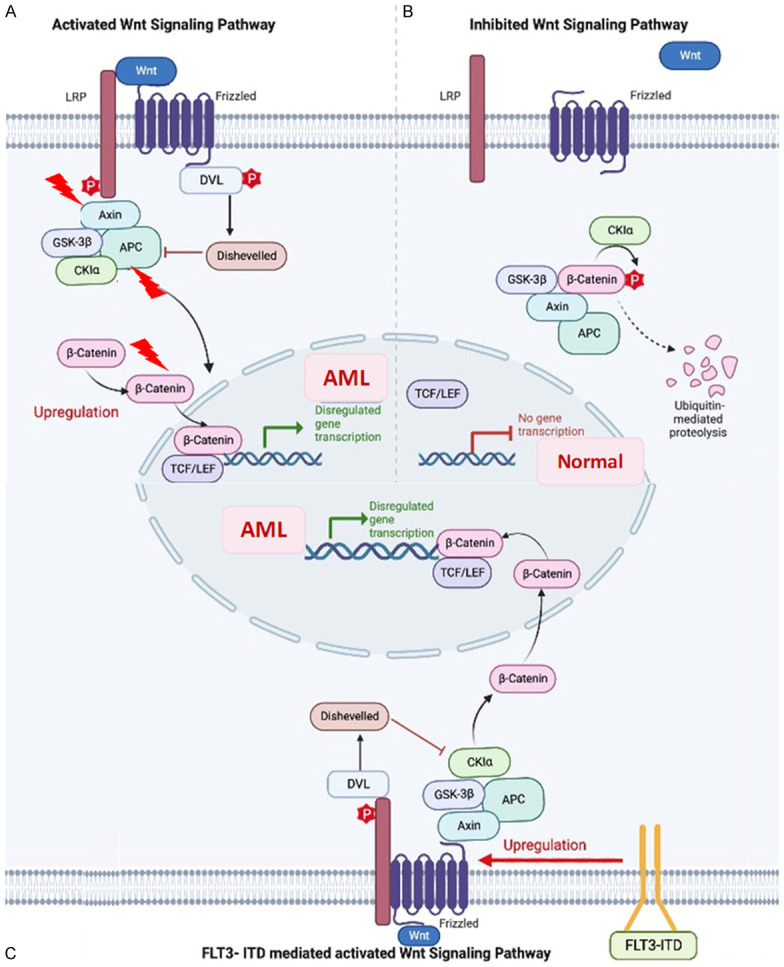
β-catenin stabilization mechanism leading to abnormal hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) proliferation. A. Wnt binding to Frizzeled (fzd) receptors and with Lipoprotein receptor-related proteins 5/6 (LRP5/6) co-receptors, activates the signalling pathway leading to the stabilization of β-catenin additionally, the mutations in Axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and β-catenin genes can impair the downregulation of β-catenin which leads to dysregulated gene transcription and abnormal HSC differentiation. B. Normal gene transcription by phosphorylation of β-catenin and its subsequent ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. C. Pathway of AML pathogenesis, in the presence of FLT3-ITD (Internal Tandem Duplication) mutations induced FZD expression and increased β-catenin nuclear localization.
