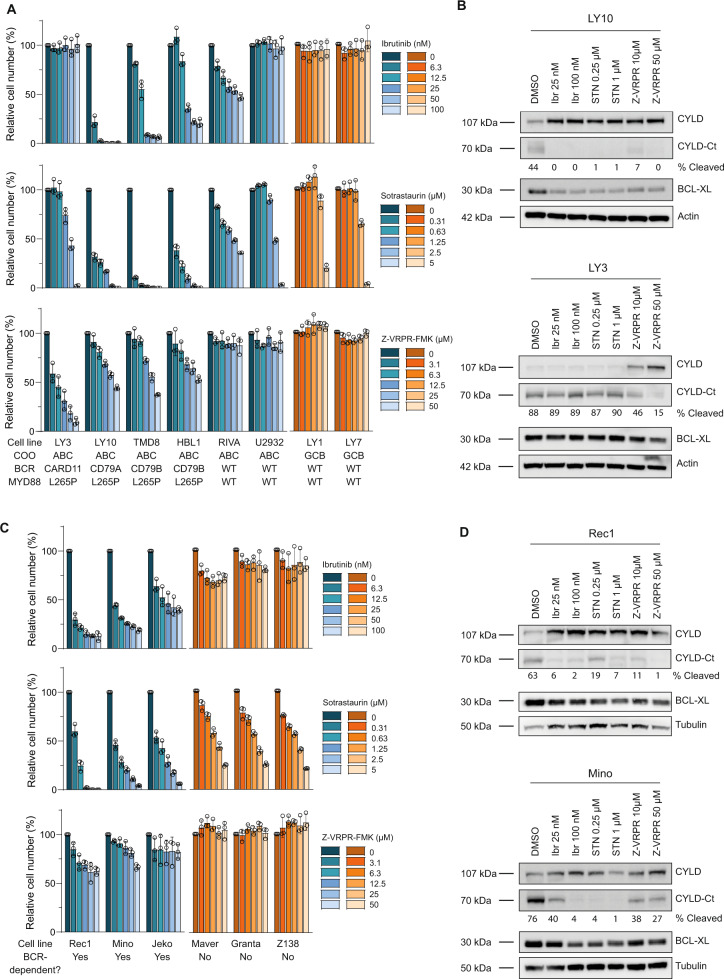
Fig. 3. CYLD is constitutively cleaved in ABC DLBCL and BCR-dependent MCL cell lines.
A Flow cytometric analysis of the number of viable cells, as determined by 7-AAD staining, after 5 days of treatment with indicated concentrations of BTK inhibitor Ibrutinib, PKC inhibitor Sotrastaurin or MALT1 inhibitor Z-VRPR-FMK. The number of viable cells was normalized to the vehicle-treated condition. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. B Immunoblot analysis of CYLD cleavage in DLBCL cell lines LY3 and LY10 using an antibody raised against a C‐terminal epitope which detects full-length CYLD and a C‐terminal fragment of CYLD (CYLD‐Ct). Cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of the different BCR signalosome inhibitors for 48 h. BCL-XL protein levels were determined as a positive control for efficacy of the inhibitors; β-actin was used as loading control. C Flow cytometric analysis of the number of viable cells, as determined by 7-AAD staining, after 7 days of treatment with indicated concentrations of BTK inhibitor Ibrutinib, PKC inhibitor Sotrastaurin or MALT1 inhibitor Z-VRPR-FMK. The number of viable cells was normalized to the vehicle-treated condition. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. D Immunoblot analysis of CYLD cleavage in MCL cell lines Rec1 and Mino using an antibody raised against a C‐terminal epitope which detects full-length CYLD and a C‐terminal fragment of CYLD (CYLD‐Ct). Cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of the different BCR signalosome inhibitors for 72 h. BCL-XL protein levels were determined as a positive control for efficacy of the inhibitors; β-tubulin was used as loading control.