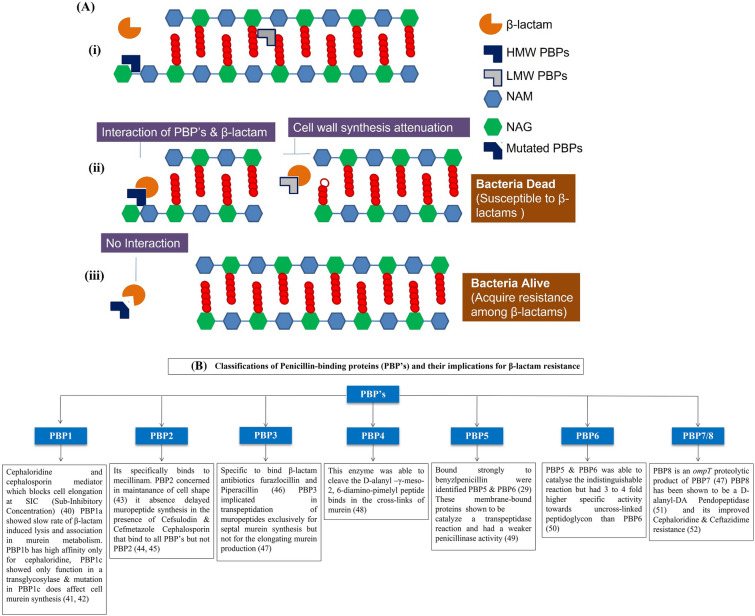
Fig. 1.
A Cell wall biosynthesis involves the assembly of peptidoglycan into strands by glycosyltransferase function [linking the lipid-bound N-acetyl glucosamine (NAM) with the pentapeptide-bound N-acetyl muramic acid (NAG)] followed by cross-linking of the assembled peptidoglycan by transpeptidase activity. Peptidoglycan glycosyltransferases catalyze the glycosyltransferase, while transpeptidase activity is PBP mediated. The high-molecular-weight (HMW) PBS is involved in both glycosyltransferase and transpeptidase functions, while the lower-molecular-weight (LMW) PBP performs only the transpeptidase function. (i) Entry of β-lactam into the site of cell wall synthesis. (ii) PBP’s arrest by β-lactam interaction. (iii) Structural alterations in PBPs due to mutation(s) affect their affinity to β-lactam, which therefore could not bind to PBPs; thus, cell wall synthesis continues. B Classifications of penicillin-blinding proteins (PBPs) and their implications