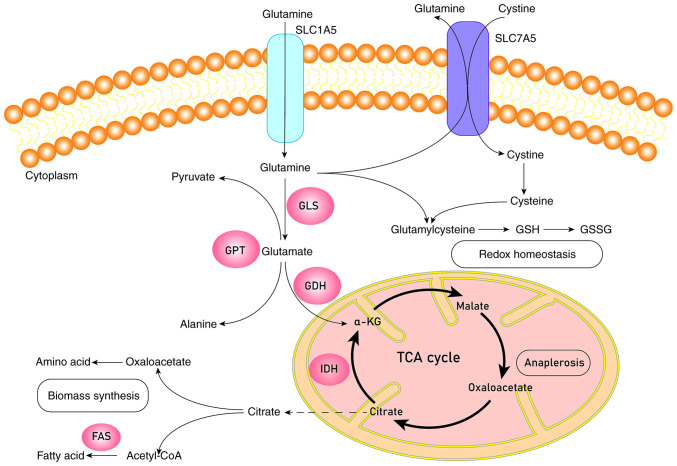
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of glutamine metabolism. Glutamine is transported into the cell by SLC1A5 or SLC7A5 and turns into glutamate catalyzed by transaminases or GLS. Glutamate will be catalyzed by GDH to generate α-KG. α-KG can enter into the TCA cycle to complete the process of anaplerosis or be catalyzed by IDH to produce citrate, which leaves mitochondria for the biomass synthesis of fatty acids and amino acids. Glutamine and cystine will synthesize glutathione through a series of catalytic processes to keep redox homeostasis. GLS, glutaminase; GPT, glutamic pyruvic transaminase; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; FAS, fatty acid synthase; GSH, glutathione (reduced); GSSH, glutathione (oxidized); α-KG, α-ketoglutaric acid; TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle.