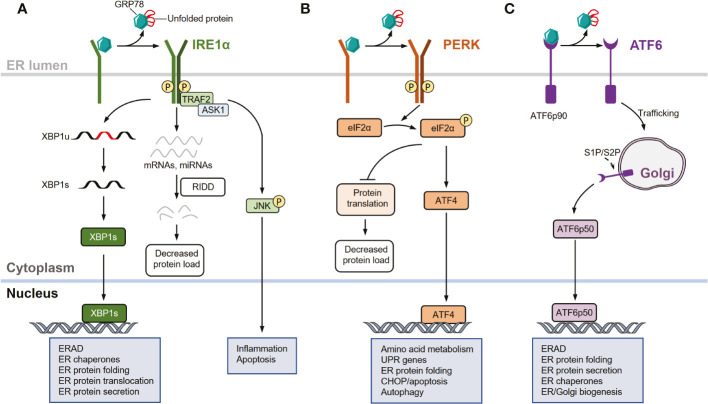
Figure 1.
UPR signaling pathways. (A) Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1α) signaling arm of the unfolded protein response (UPR). In response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, IRE1α is activated through dissociation from glucose- regulated protein 78 (GRP78), oligomerization, autophosphorylation, and subsequent allosteric activation of the cytosolic endonuclease domain. Activated IRE1α facilitates the unconventional splicing of XBP1 (XBP1u) mRNA, resulting in active transcription factor XBP1s, which drives the expression of genes involved in restoring ER homeostasis. IRE1α also degrades select mRNAs and miRNAs through regulated IRE1-dependent decay (RIDD) to reduce protein load in the ER during intensive ER stress. In response to severe or unresolved ER stress, activated IRE1α recruits and binds to tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) to promote c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling, leading to the activation of apoptosis. (B) Protein kinase R (PKR)-like ER kinase (PERK) arm of the UPR. In response to ER stress, PERK is activated by dissociating from GRP78 and auto-phosphorylating after dimerization. Activated PERK selectively phosphorylates eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit-α (eIF2α), thereby attenuating protein translation. The mRNA of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) is preferentially translated following eIF2α phosphorylation, allowing it to upregulate genes involved in restoring ER homeostasis, amino acid metabolism, apoptosis, and autophagy. (C) Activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) arm of the UPR. In response to ER stress, GRP78 dissociates from the luminal domain of full-length of ATF6 (ATF6p90), allowing ATF6 monomers to traffic to the cis-Golgi apparatus where they are proteolytically processed and cleaved by site-1 protease (S1P) and site-2 protease (S2P). This releases an active ATF6 transcription factor fragment (ATF6p50). The transcription factor localizes to the nucleus, inducing several genes involved in restoring ER homeostasis and ER/Golgi biogenesis.