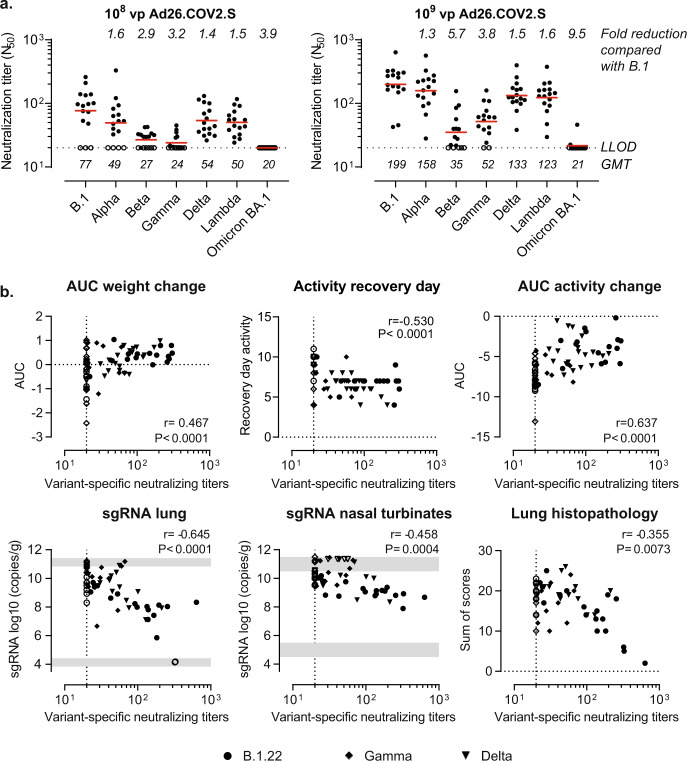
Fig. 3. Correlation of vaccine efficacy parameters with neutralizing antibody titers.
Hamsters were vaccinated with formulation buffer (mock), 108 or 109 vp Ad26.COV2.S at day −28. Sera were collected before the challenge at day 0 to measure neutralizing titers against pseudotyped viruses expressing SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants in a pseudotyped virus neutralization assay (psVNA). Neutralizing antibody titers are expressed as the dilution giving a 50% reduction (N50) in the normalized luciferase readout. a Neutralizing antibody titers are shown for various spike protein variants. b Hamsters were intranasally challenged with 103 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 B.1.22, 104 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 Gamma, or 104 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 Delta on day 0. The correlation between neutralizing antibody titers homologous to the challenge strain (B.1 nAbs for B.1.22 challenge, P.1 nAbs for Gamma challenge, and B.1.617.2 nAbs for Delta challenge) in animals vaccinated with Ad26.COV2.S or formulation buffer (mock) with weight change, activity change (recovery day and AUC), lung histopathology, and SARS-CoV-2 Envelope subgenomic RNA (sgRNA) viral load in the lungs and nasal turbinates is shown. Correlation coefficients were calculated across all 3 VOC using a two-sided Spearman rank correlation. Red horizontal bars indicate the geometric mean titers (GMT) and the dotted line/gray zone indicates the limit of detection (LOD) or LOD range. Open symbols indicate the response is at or below the lower LOD (LLOD)/at or above the upper LOD (ULOD).