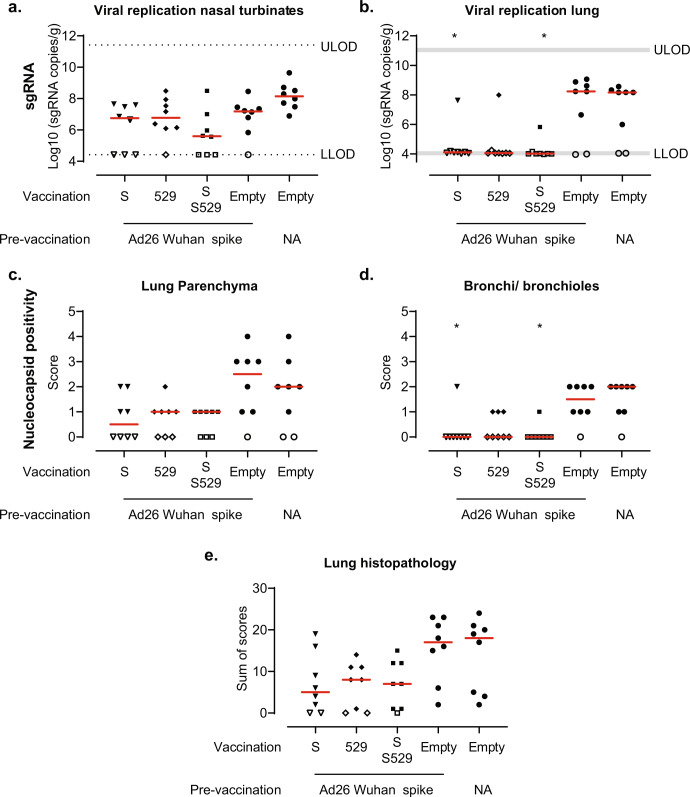
Fig. 6. Protection against the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 variant.
Hamsters with pre-existing immunity were generated by pre-vaccination with 107 viral particles (vp) of Ad26NCOV006 (Ad26 vector encoding Wuhan-Hu-1 spike, pre-immune animals) at week −27. Naive control hamsters were not vaccinated (NA). At week −4, Ad26 Wuhan-Hu-1 spike-vaccinated hamsters were vaccinated with 109 vp Ad26.COV2.S (S), Ad26.COV2.S.529 (529), a 1:1 combination of S and 529 or Ad26.Empty (all n = 8). In addition, naive hamsters were vaccinated with Ad26.Empty (n = 8). The animals were intranasally challenged with 104.7 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 in week 0. SARS-CoV-2 Envelope subgenomic RNA (sgRNA) viral load was measured in the a nasal turbinates and b lungs. c/d Lungs (parenchyma and bronchi/bronchioles) were stained and scored for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid-protein positivity (score 0–5). e Paraffin sections from lung tissue (H&E) were scored on day 4 for lower tract histopathology. The sum of scores is presented (maximum possible score of 48). Red horizontal bars indicate the median response per group and the dotted line/gray zone indicates the limit of detection (LOD) or LOD range. Open symbols indicate the response is at or below the lower LOD (LLOD)/at or above upper LOD (ULOD) or a score of 0 for nucleocapsid positivity or histopathology. Comparisons to the pre-vaccination-only group and pairwise comparisons were performed by a Mann–Whitney U test with a threefold Bonferroni correction. Significance is shown compared with the pre-vaccinated-only group unless depicted otherwise. Statistical differences are indicated by asterisks: *P < 0.05.