Figure 7. Sites of LYS tethering on LEs contain HOPS and Rab2 but not Rab7.
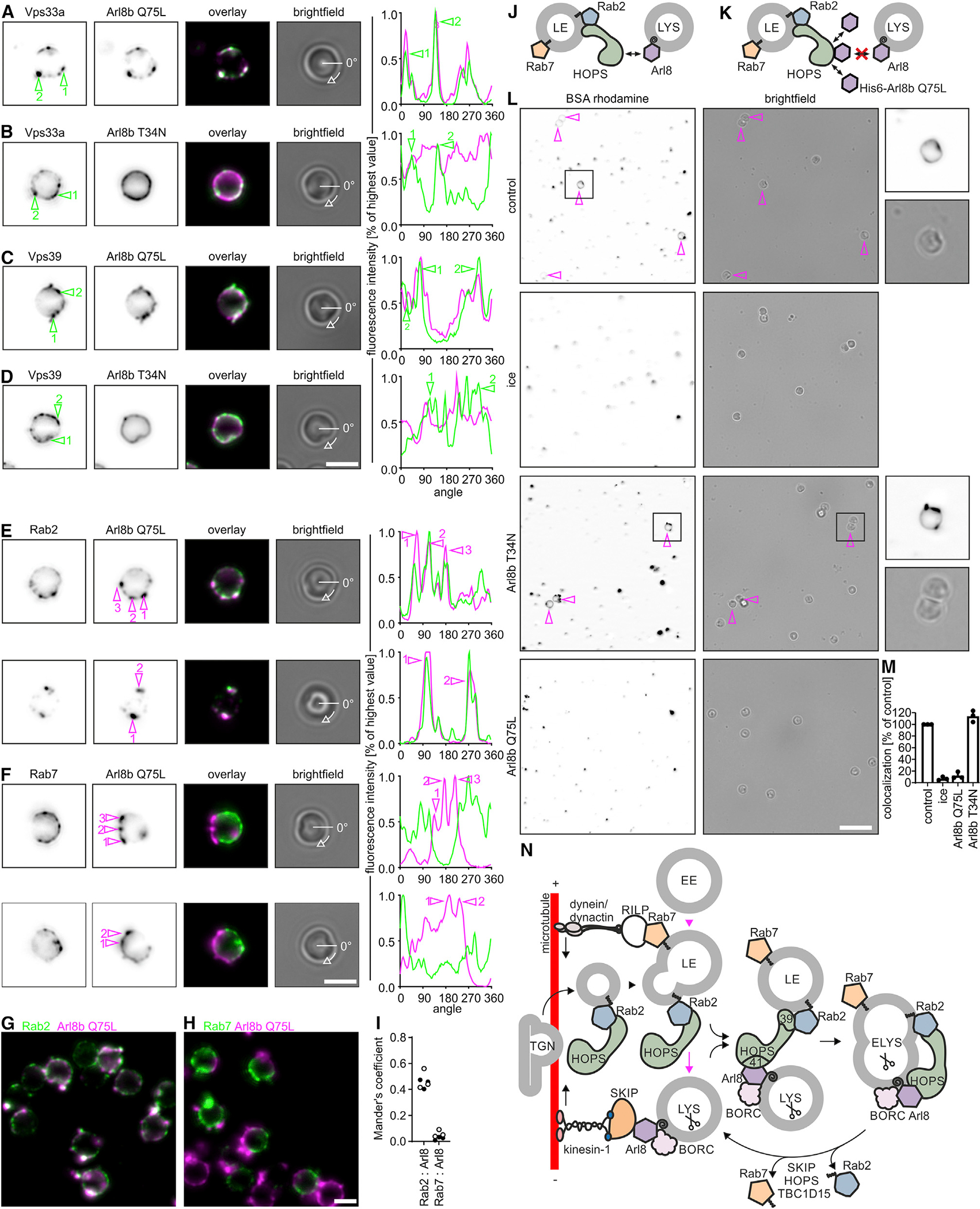
(A–D) Purified late LBPs were incubated with and stained for bound Arl8b(Q75L) (A and C) or Arl8b(T34N) (B and D) and for HOPS (Vps33a, A and B, or Vps39, C and D). Representative fluorescence micrographs. Fluorescence intensities along the circumference of the phagosome for Arl8 or HOPS staining were plotted against the rotation angle, starting at 0 degrees as marked in the bright-field images. Sites of HOPS enrichment are numbered and highlighted in micrographs and fluorescence intensity plots.
(E and F) Similar to (A)–(D), but phagosomes were stained for Arl8b(Q75L) and endogenous Rab2a (E) or Rab7 (F). Sites of Arl8 binding are marked. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. Bar: 2 μm.
(G and H) Larger sections of representative micrographs from experiments in (E) and (F). Bar: 2 μm.
(I) Mander’s coefficients for the overlap between Rab2a or Rab7 and Arl8b(Q75L). Data points refer to Mander’s coefficients determined for each one micrograph with >10 phagosomes. Black and white data points display results from 2 independent experiments.
(J) Hypothesis how LE-LYS tethering works.
(K) Experimental setup to identify Arl8b(Q75L)-binding sites on LEs as sites of LYS tethering.
(L) Late LBPs were preincubated with purified Arl8b(Q75L) or Arl8b(T34N) and tested for fusion with BSA-rhodamine-loaded LYSs. Representative micrographs. Bar: 10 μm. Magenta arrows indicate LBPs colocalizing with the LYS fluor. Boxed areas are shown at higher magnification.
(M) Colocalization of LBPs with BSA-rhodamine. Data are means ± SD from 3 independent experiments.
(N) Working model of endosome maturation. See main text for details. Scissors indicate the presence of mCathD in ELYSs and LYSs. SNAREs have been omitted for reasons of clarity.
