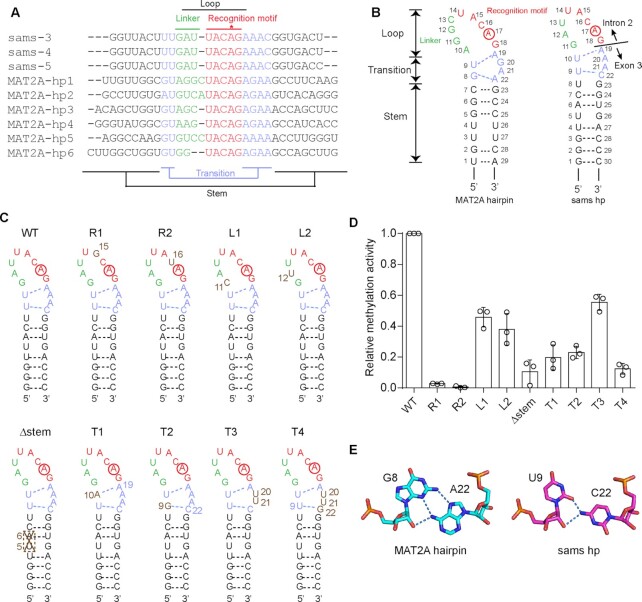
Figure 3.
RNA recognition by C. elegans METT10. (A) Alignments of the nucleotide sequences around the junction between intron 2 and exon 3 of C. elegans sams (-3, -4 and -5) pre-mRNAs and the 3'-UTR hairpin regions of human MAT2A (MAT2A-hp1–6) pre-mRNAs (31). (B) Secondary structures of 3'-UTR hairpin RNA (MAT2A-hp1) of human MAT2A pre-mRNA (left) and C. elegans sams hairpin RNA spanning intron 2 and exon 3, including the 3'-splice site (AG-dinucleotides) (right). The sams RNA also adopts a hairpin structure (sams-hp), as in human MAT2A-hp1. The adenine residues targeted for methylation are circled. The hairpin comprises the loop, transition, and stem regions (23). The loop region is composed of the recognition motif (UACAG: red) and linker (green). (C) Secondary structures of C. elegans sams-hp RNA and its variants used for the methylation assays in (D). (D) Methylation of sams-hp RNA and its variants by METT10-FLΔL. The sams-hp RNA (1 μM) and its variants were each incubated with 0.4 μM METT10-FLΔL in the presence of 1 mM SAM, at 37°C for 4 min. The methylation of wild-type sams-hp RNA by METT10-FLΔL was taken as 1.0. The bars in the graph are the SD of three independent experiments. (E) G8–A22 base pairing in the transition region near the stem of hMAT2A-hp (left) and the possible U9–C22 base pairing at the corresponding position in the sams-hp (right). Possible hydrogen bonds between the sugar edge of U9 and the 4-NH2 group of C22 are depicted by dashed lines.