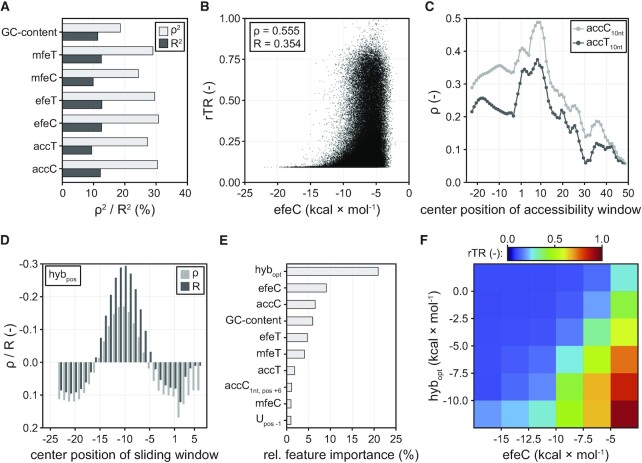
Figure 3.
Effect of different sequence parameters on translation initiation in Librandom. (A) Correlation of GC-content and different mRNA folding metrics with rTR. Spearman's ρ2 and Pearson's R2 are displayed. (B) Scatterplot between rTR and the best-correlating mRNA folding parameter efeC. (C) Correlation of rTR with local mRNA accessibility. Parameters accT10nt and accC10nt correspond to the mRNA accessibility of a 10-nt window centred around the mRNA position specified on the horizontal axis. Endings C and T denote base pairing calculated by two different energy models (Methods). (D) Correlation of hybridisation energy between 16S rRNA and different mRNA positions with rTR. Positional hybridisation energy (hybpos) is displayed for 9-bp windows centred around the indicated mRNA position (horizontal axis). (E) Relative feature importance of a random forest model trained on Librandom. The ten most important of 248 features are displayed. hybopt: best-correlating hybridisation parameter (see main text). accC1nt, pos+6: accC score for position +6 of the mRNA. Upos –1: one-hot encoded U at position −1 of the mRNA. (F) Mean rTR of variants in Librandom as grouped by the two most predictive features of the random forest, hybopt and efeC. Tick labels mark the boundaries of the respective bins (boxes).