Figure 3. Difference in the microbial community between patients with CN and CI.
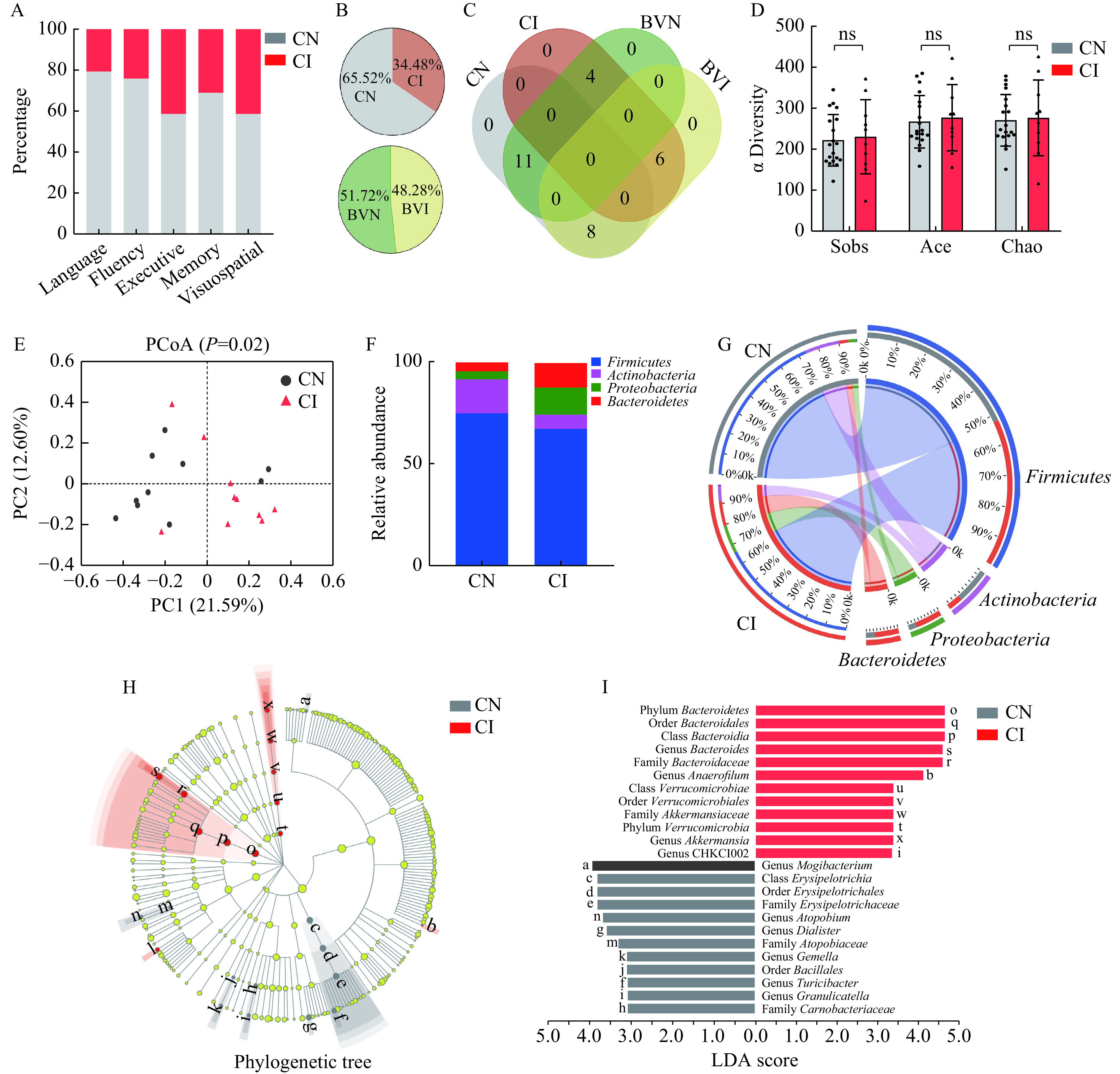
A–C: Cognitive function of patients with ALS in the current study. Frequency of patients with CI in five subdomains of ECAS (A). Frequency of patients with CI and behavioral impairments (B). Coexistence of CI and behavioral impairments in patients with ALS (C). D: Comparison of microbial α diversity between the CN and CI groups (assessed by Sobs, Ace, and Chao index). E: Comparison of microbial β diversity between the CN and CI groups (assessed by PCoA). F and G: Relative abundance of the microbial community at phylum level between CN and CI. H and I: Distinguishing bacterial taxa between the CN and CI groups was identified by LEfSe analysis. Cladogram showing the phylogenetic distribution of the bacterial lineages. Circles indicate phylogenetic levels from domain to genus. The diameter of each circle is proportional to the abundance of the bacterial group (H). The letters show the distinguishing taxa with a LDA score >3 (I). ns: not significant; ECAS: Edinburgh Cognitive and Behavioral ALS Screen; CN: normal cognition; CI: cognitive impairments; BVN: behavior normal; BVI: behavior impaired; PCoA: Principal coordinates analysis; LEfSe: the Linear discriminant analysis of effect size.
