Figure. 1. Potential mechanisms of renal mitochondrial damage in hypertensive and diabetic CKD.
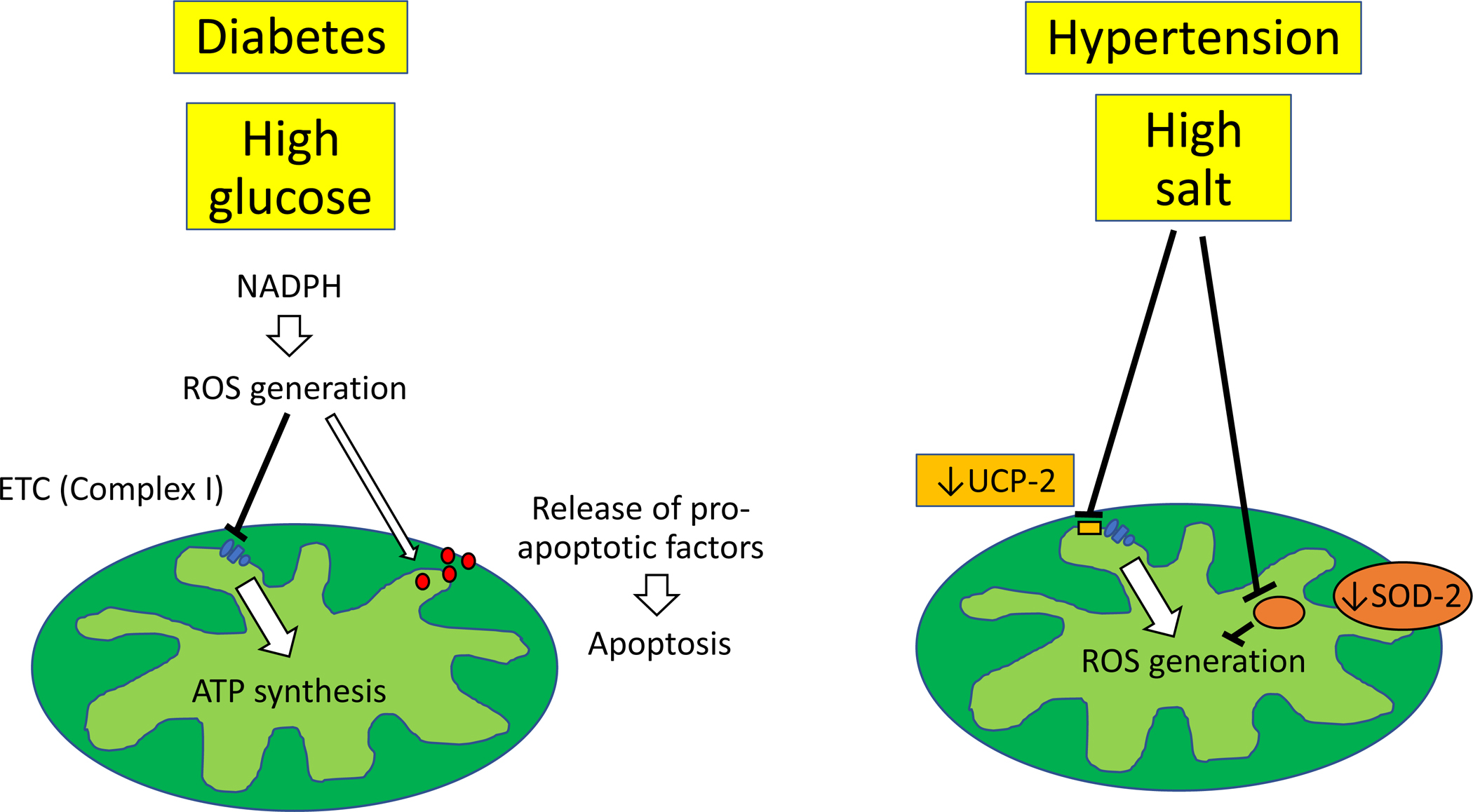
Exposure of podocytes to high glucose results in apoptosis and NADPH superoxide generation. This in turn inactivates mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I and favors release of pro-apoptotic factors, contributing to impaired bioenergetics and apoptosis. A high salt diet induces structural mitochondrial abnormalities and impaired bioenergetics, associated with reduced expression of uncoupling protein-2 and increased production of ROS.
