Figure 2. Antibodies in NK cell immunotherapy.
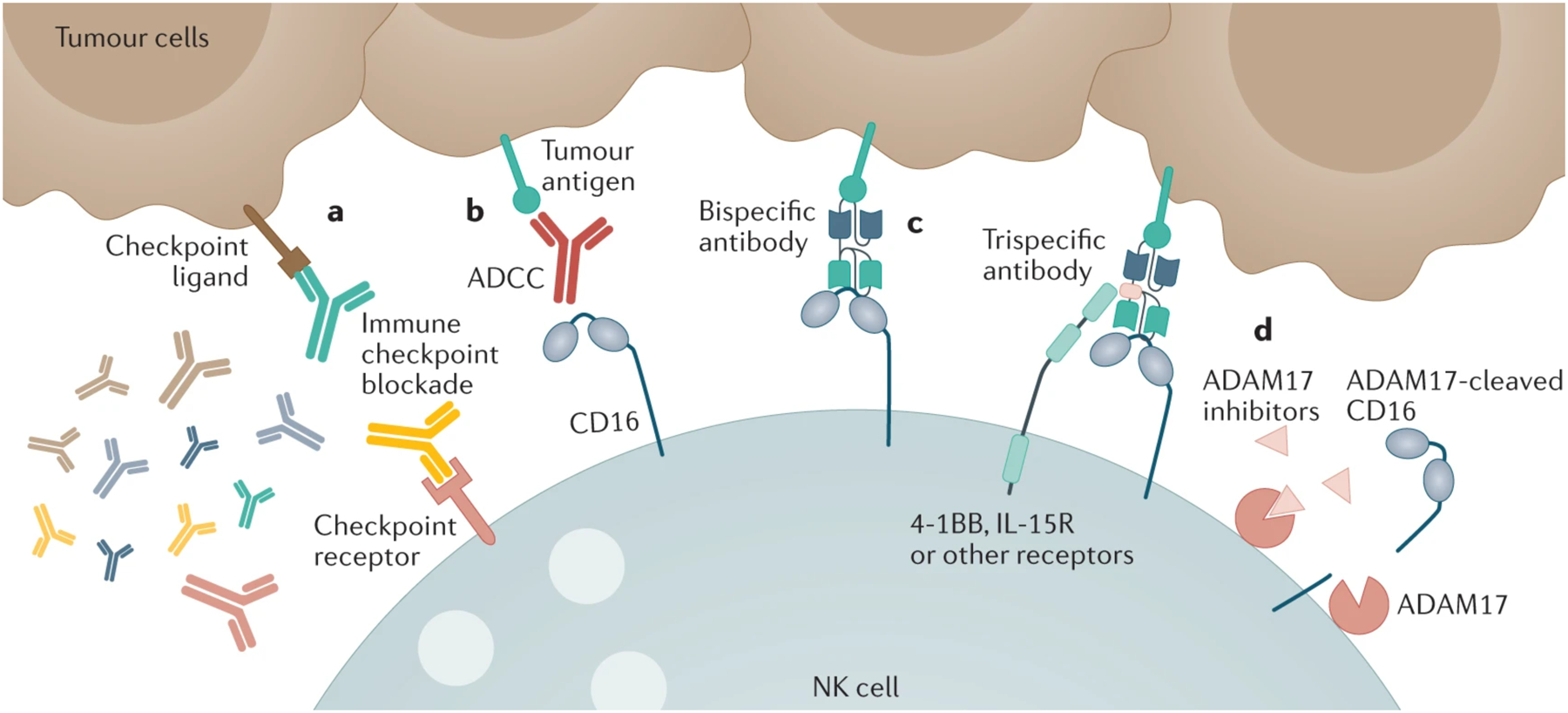
Antibodies can be used to enhance NK cell function in several different ways. a. Immune checkpoint blockade can be used to prevent the engagement of checkpoint inhibitory receptors on NK cells with their ligands on tumours. b. Antibodies targeting tumour antigens can be engaged via their Fc domains with CD16 on the surface of NK cells, triggering ADCC. c. Next generation bi- and tri-specific antibody constructs have also been designed that more efficiently engage with CD16 (and/or other activating receptors) than classic antitumour monoclonal antibodies. d. Finally, it is being investigated whether inhibitors of the metalloprotease ADAM17 can enhance ADCC by preventing the cleavage of CD16. The diversity of therapeutic strategies on display means they can often be used in tandem to activate NK cells through the interaction of multiple signaling pathways, although targeting the NK cell to the tumour is critical.
