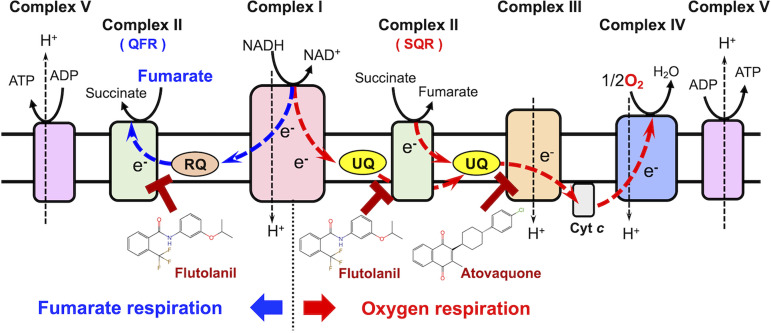
FIG 1.
Overview of the mitochondrial respiratory chain of E. multilocularis. Fumarate respiration (NADH:fumarate reductase system) involves complex I, rhodoquinone (RQ), and complex II (quinol:fumarate reductase, QFR). In this system, electrons from NADH are transferred to RQ through complex I, and then transferred to fumarate by the QFR activity of complex II. An electrochemical gradient is maintained by the activity of complex I, and ATP is generated by oxidative phosphorylation (complex V) even under hypoxic conditions. Oxygen respiration is performed by complexes I, II, III, and IV, with ubiquinone (UQ) acting as an electron carrier between complexes I/II and III, and cytochrome c (Cyt c) between complexes III and IV. Complex II transfers electrons from succinate to UQ, acting as a succinate:quinone reductase (SQR). At the end of oxygen respiration, the electrons from NADH and succinate are used to reduce oxygen molecules to form water. Flutolanil and atovaquone are quinone binding site inhibitors of complexes II and III, respectively.